Haven’t had much luck finding Unit 3 QCAA Chemistry practice questions for your IA1 Data Test?
Well today’s your lucky day, because we’ve got 25 practice questions you can use in preparation for your actual Unit 3 Chemistry Data Test!
Wondering how to prepare for your other internal assessments? We’ve got everything you need to know about your QCE IA1s.
You’ll also be able to check your answers after completing these practice questions with our downloadable solutions.
Why you need a 10/10 on the Chemistry Data Test to be on track for an ATAR over 90…
So what are you waiting for? Let’s get started!
Data Set 1
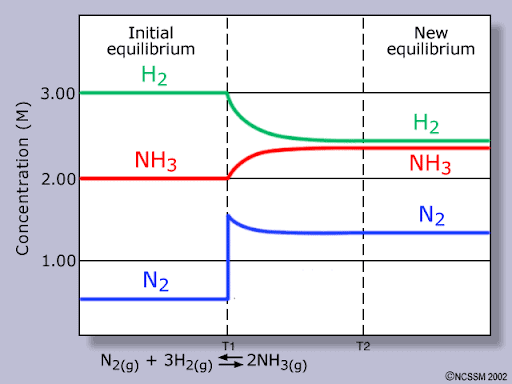
A closed reaction vessel contains nitrogen (0.5M), hydrogen (3.0M) and ammonia (2.0M) at equilibrium:
N2(g)+3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Image sourced from Socratic Q&A
Question 1 (2 marks)
Deduce what has happened to the equilibrium position, with reference to Le Chatelier’s principle, at T1.
Question 2 (1 mark)
Deduce what has happened to the equilibrium position at T2.
Question 3 (4 marks)
(a) Describe the effect on the equilibrium position of all reactants and products, with reference to Le Chatelier’s principle, if the hydrogen concentration was increased.
(b) Describe the effect on the equilibrium position, with reference to Le Chatelier’s principle, if the ammonia concentration was increased.
Question 4 (1 mark)
Supposing that the enthalpy for the reaction in Question 1 is ∆H = –91kJmol-1, determine whether it is an exothermic or endothermic reaction.
Question 5 (2 marks)
(a) Using the answer from Question 4 to justify, explain what would happen to the equilibrium position of the reactions if the temperature of the system was increased.
(b) Using the answer from Question 4 to justify, explain what would happen to the equilibrium position of the reactions if the temperature of the system was decreased.
Question 6 (4 marks)
(a) Explain what effect increasing the pressure inside the system would have on the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier’s principle.
(b) Explain what effect decreasing the pressure inside the system would have on the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier’s principle.
(c) Explain what effect increasing the volume inside the system would have on the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier’s principle.
(d) Explain what effect decreasing the volume inside the system would have on the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier’s principle.
Question 7 (1 mark)
Explain what effect adding a catalyst to the system would have on the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier’s principle. Give a reason as to why.
Data Set 2
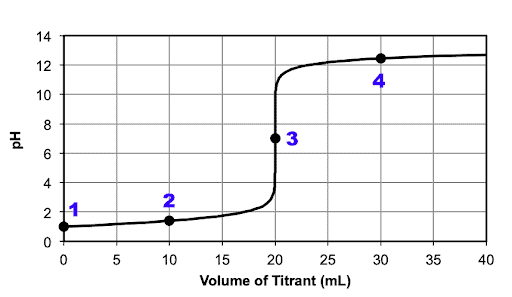
Image sourced from University of Wisconsin Pressbooks
Question 1 (1 mark)
Investigate Data Set 2 and determine what type of titration it represents (use the terms strong/weak and acid/base).
Question 2 (1 mark)
Determine the pH of the titrant and what number (1-4) on the graph it is represented by.
Question 3 (1 mark)
Determine the pH of the titrand and what number (1-4) on the graph it is represented by.
Question 4 (1 mark)
Determine the pH of the half-equivalence point and what number (1-4) on the graph it is represented by.
Question 5 (1 mark)
Determine the pH of the equivalence point and what number (1-4) on the graph it is represented by.
Question 6 (3 marks)
Distinguish between the half-equivalence point and equivalence point in terms of the pH and volume of the titrant.
Question 7 (3 marks)
Distinguish between the equivalence point and end point.
Question 8 (2 marks)
Determine the most appropriate pH indicator for this titration using your Formula and data book. Provide reasoning.
Data Set 3
| Strongest to weakest oxidising agent (1-8) | Half-reaction | E° (V) |
|---|---|---|
| AuCl4-(aq) + 3e- ⇌ Au(s) + 4Cl-(aq) | +1.00 | |
| F2(g) + 2e- ⇌ 2F-(aq) | +2.89 | |
| NO3-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 3e- ⇌ NO(g) + 2H2O(l) | +0.96 | |
| Mg2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Mg(s) | -2.36 | |
| Br2(l) + 2e- ⇌ 2Br-(aq) | +1.08 | |
| Ni2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Ni(s) | -0.24 | |
| Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Cu(s) | +0.34 | |
| Zn2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Zn(s) | -0.76 |
Question 1 (2 marks)
According to the standard reduction potentials (E°) provided in Data Set 3, order the half-reactions from strongest to weakest oxidising agent (1-8).
Question 2 (2 marks)
Comparing the following half-reactions, determine which is the strongest oxidant and which is the strongest reductant. Use the E° values to support your answer.
- Half-reaction 1(a): F2(g) + 2e– ⇌ 2F–(aq)
- Half-reaction 1(b): Ni2+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ Ni(s)
Question 3 (2 marks)
Using the E° values provided, calculate the EMF of a fluoride-nickel galvanic cell.
Question 4 (2 marks)
Comparing the following half-reactions, determine which is the strongest oxidant and which is the strongest reductant. Use the E° values provided to support your answer.
- Half-reaction 2(a): Cu2+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ Cu(s)
- Half-reaction 2(b): Zn2+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ Zn(s)
Question 5 (2 marks)
Write the oxidation half-reaction for half reaction 2(a).
Question 6 (2 marks)
Determine, in a spontaneous redox reaction between half reaction 2(a) and half reaction 2(b), which of the chemical species will react.
Question 7 (3 marks)
Determine the equation for the balanced chemical reaction between half reaction 2(a) and half reaction 2(b).
Data Set 4
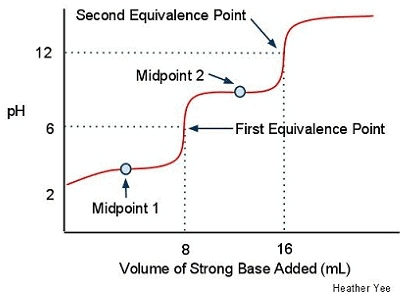
Image sourced from LibreTexts
Question 1 (2 marks)
Label the buffer region(s).
Question 2 (1 mark)
Explain what the presence of two equivalence points suggests about the acid in this titration.
Question 3 (1 mark)
Provide an example of a common diprotic or polyprotic acid.
QCAA Unit 3 Chemistry Data Test Practice Solutions
On the hunt for other QCAA Chemistry resources?
Get a head start by knowing where you sit in comparison to your peers! Check out our FREE Cohort Comparison Tool to show you exactly how you’re really doing!
We’ve got plenty more practice questions for you to use to revise previous content from throughout the year! Check them out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Term 1 of Year 12 Including all the Key Resources You Will Ever Need
- Practice Questions for Unit 3 & 4 Chemistry External Assessment
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions for Unit 3 & 4 Chemistry External Assessment
- Download QCAA Chemistry Practice Exam for External Assessment Revision
You’ll also want to have a look at our nifty guides for working on your QCAA Chemistry assessments below:
- The Definitive Guide to Writing a Student Experiment Report for QCAA Chemistry
- The Ultimate Guide to Conducting a QCAA Chemistry Research Investigation
- How to Ace Your External Assessment for QCAA Chemistry
- The Ultimate Guide to QCAA Chemistry Unit 3: Equilibrium, Acids and Redox Reactions
- The Ultimate Guide to QCAA Chemistry Unit 4: Structure, Synthesis and Design
Is IA1 for you coming up at the end of Year 11? Save yourself some headaches and read these 5 Tips for how to ACE IA1 in Year 11!
Are you looking for some extra help with the Unit 3 QCAA Chemistry Data Test IA1?
We have an incredible team of QCE tutors and mentors!
We can help you master the QCAA Chemistry syllabus and ace your upcoming Chemistry assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational QCE tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Yalindi Binduhewa is an Art of Smart tutor based in Queensland and was part of the very first cohort to go through the ATAR system, so she knows exactly how fun and enjoyable it can be. She is currently studying a Bachelor of Medical Imaging (Honours) at QUT and is loving it. When she’s not doing uni-related stuff or tutoring, she’s hanging out with her friends, rewatching a show for the 100th time, or trying out new crafty projects and discovering that she doesn’t have a talent for everything.