Done with Unit 3 of QCAA Chemistry and are beginning to work on Unit 4?
To help you develop an understanding of what you’ll be learning in this unit, we’ll break down all of the topics you’ll be taking on and provide you with guides on how to complete your assessments for QCAA Chemistry Unit 4.
Ready to get started? Let’s go!
What is Unit 4 in QCAA Chemistry all about?
Topic 1: Properties and Structure of Organic Material
Topic 2: Chemical Synthesis and Design
QCE Chemistry Unit 4 Assessments
Study Tips
What is Unit 4 in QCAA Chemistry all about?
Unit 4 is the second of your two formative senior units for Chemistry. This means that the assessments you do for this unit (IA3 and EA) will count towards your ATAR.
The unit is split into two topics:
- properties and structure of organic materials
- chemical synthesis and design
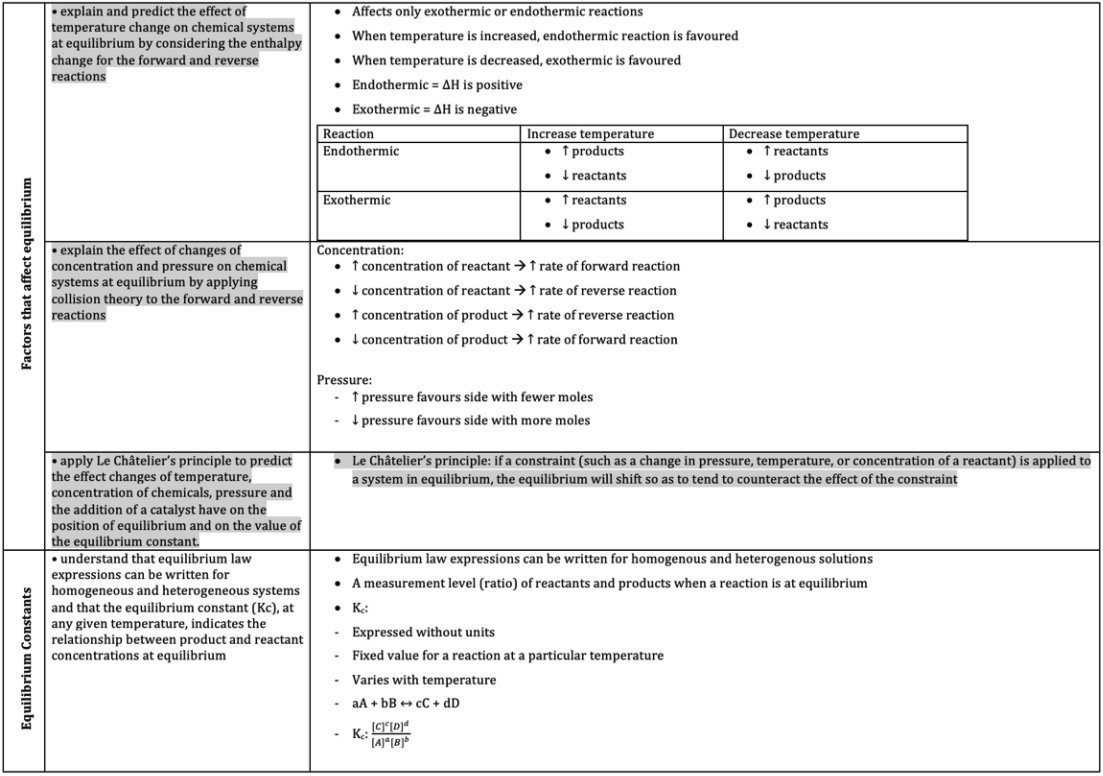
These topics cover a variety of subtopics from equilibrium constants to electrolytic cells.
Topic 1: Properties and Structure of Organic Material
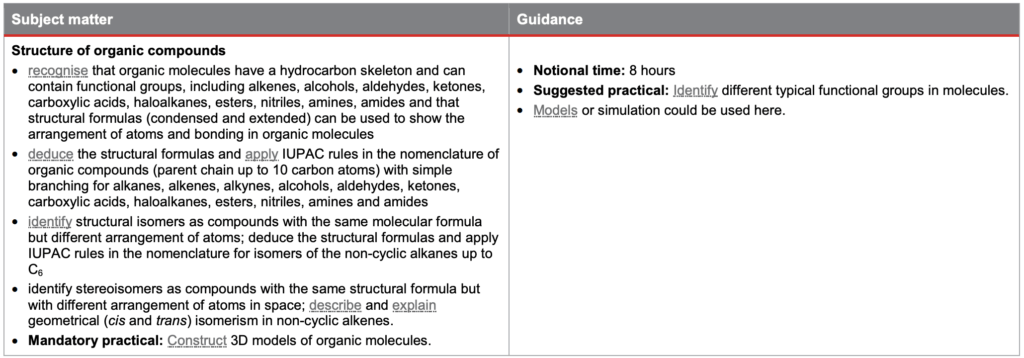
Structure of Organic Compounds
This subtopic covers:
- recognising that organic molecules have a hydrocarbon skeleton
- understanding the different functional groups
- applying IUPAC rules to name organic compounds
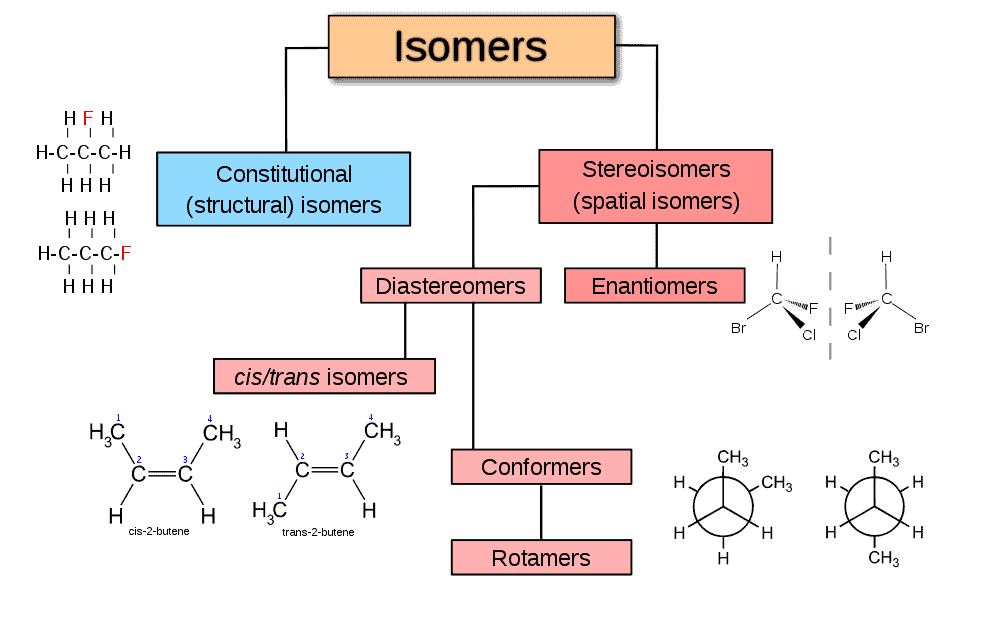
- understanding that structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms
- applying IUPAC rules to name stereoisomers
- identify stereoisomers as compounds with the same structural formula but with different arrangement of atoms in space
- understanding geometrical (cis and trans) isomerism in non-cyclic alkenes
| Number of Substituents | Multiplier |
|---|---|
| 2 | Di |
| 3 | Tri |
| 4 | Tetra |
| 5 | Penta |
| Number of Carbons | Prefix for Main Chain |
|---|---|
| 1 | Meth |
| 2 | Eth |
| 3 | Prop |
| 4 | But |
| 5 | Pent |
| 6 | Hex |
| 7 | Hept |
| 8 | Oct |
| 9 | Non |
| 10 | Dec |
IUPAC Rules
- Find and name longest continuous carbon chain (root/parent name)
- Identify and name groups attached to this chain (branches/substituent groups): 1C methyl, 2C ethyl, 3C propyl
- Number chain consecutively, starting at the end nearest a substituent group
- Designate the location of each substituent group by an appropriate number and name
- First write the names of the substituent groups in the order of <number dash name>
- If the same branch is present more than once, write the numbers first separated by commas and use ‘di tri tetra penta’ to describe them
- If different branches are present, arrange the names in alphabetical order ‘butyl ethyl methyl propyl’
- Last write the ‘root name’ which is the name of the longest chain as one word
Image sourced from Wikipedia
Physical Properties and Trends
This subtopic covers:
- recognise that organic compounds display characteristic physical properties (i.e. melting point, boiling point and solubility) that can be explained in terms of intermolecular forces
- predict and explain the trends in melting and boiling point for members of a homologous series
- understanding volatility and solubility in water of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and halides.
| Class of Compound | Intermolecular Forces | Melting/Boiling Point | Polarity & Solubility in Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkane | - dispersion force | Low | Low Non soluble |
| Alcohol | - dispersion force - hydrogen bond - dipole-dipole | High | High Soluble |
| Aldehyde | - dispersion force - dipole-dipole | Medium | Medium |
| Ketone | - dispersion force - dipole-dipole | Medium | Medium Soluble |
| Carboxylic acid | - dispersion force - dipole-dipole - hydrogen bond | Medium/High | Medium/High Soluble |
| Ester | - dispersion force - dipole-dipole | Medium | Medium |
| Amide | - dispersion force - dipole-dipole - hydrogen bond | Medium/High | Medium/High |
| Amine | - dispersion force - hydrogen bond | High | High Soluble |
| Nitrile | - dispersion force - hydrogen bond | High | High Soluble |
Organic Reactions and Reaction Pathways
This subtopic covers:
- understanding that each class of organic compound displays characteristic chemical properties and undergoes specific reactions based on the functional group present
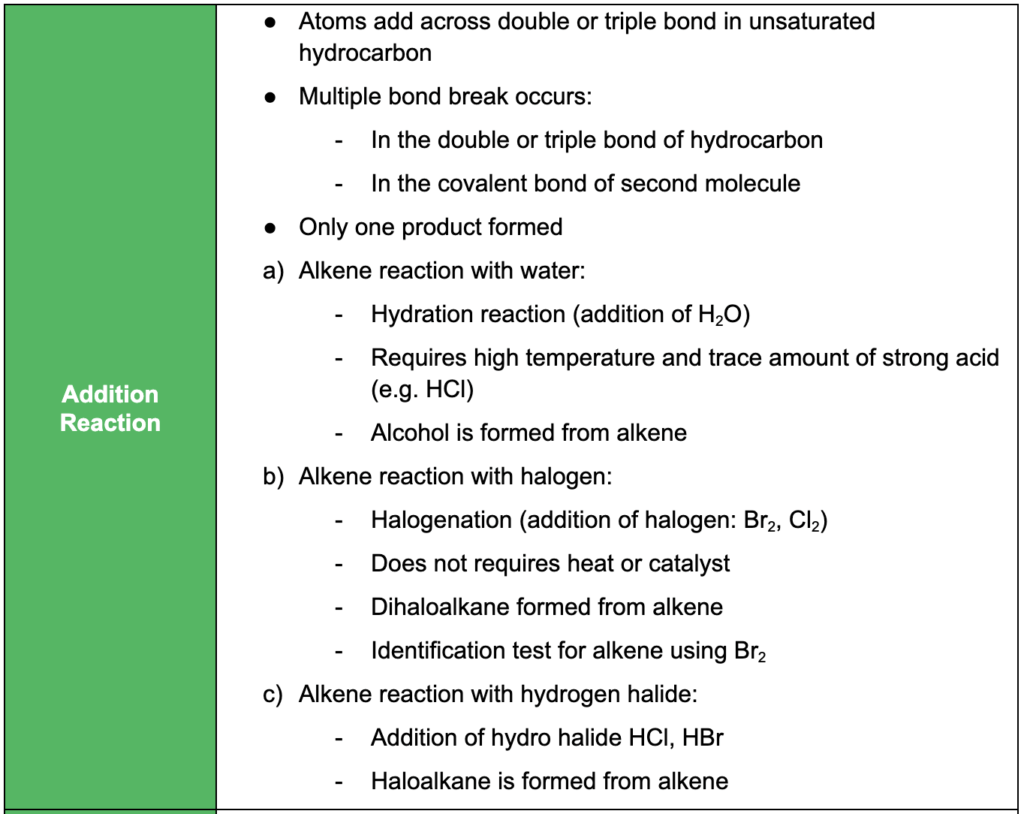
- saturated vs unsaturated compounds and their bonds and reactions
- identifying and naming the primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms in halogenoalkanes and alcohols
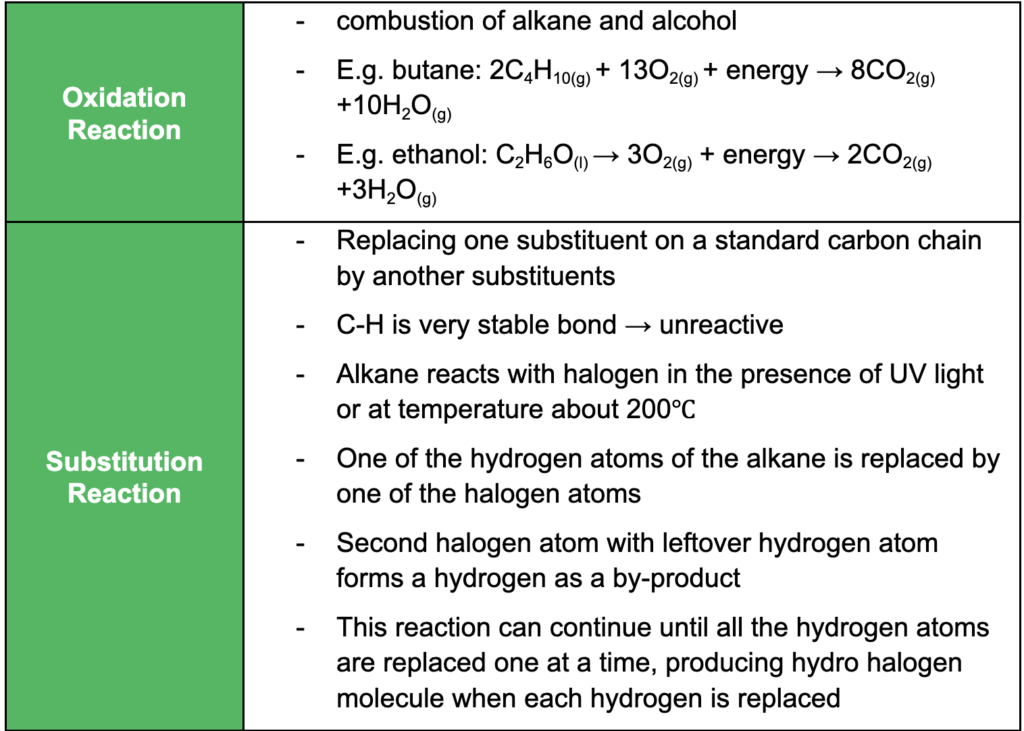
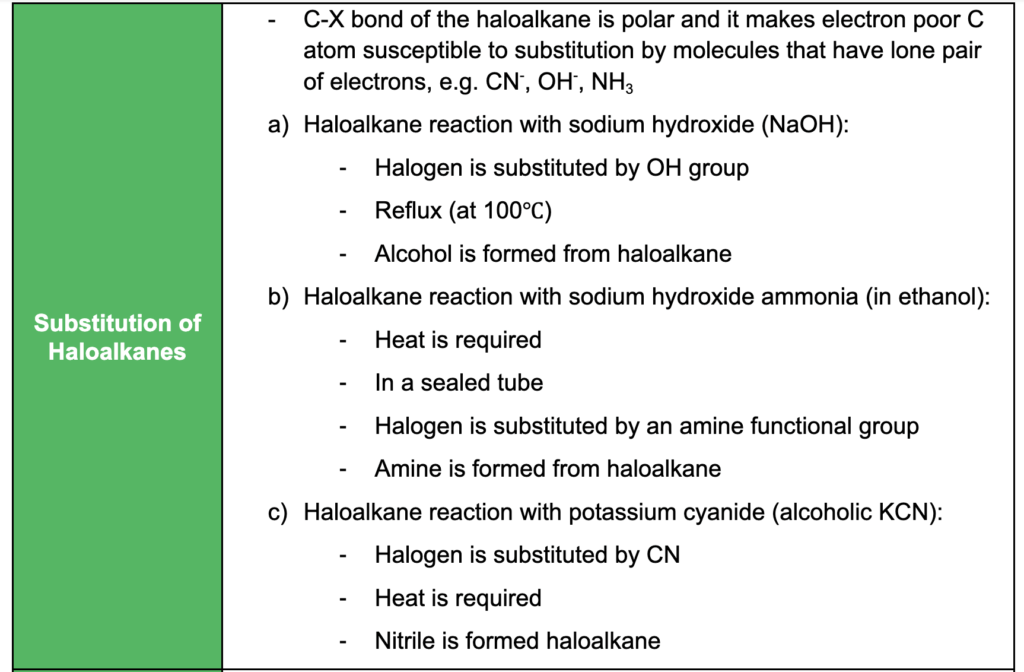
- understanding oxidation, reduction, substitution, addition, condensation and elimination reactions and relevant examples of each
- distinguishing between alkenes vs alkanes and primary vs secondary vs tertiary alcohols
- deducing reaction pathways, given the starting materials and the product
Organic Materials: Structure and Function
This subtopic covers:
- using primary, secondary and tertiary structures of organic materials to explain properties including strength, density and biodegradability
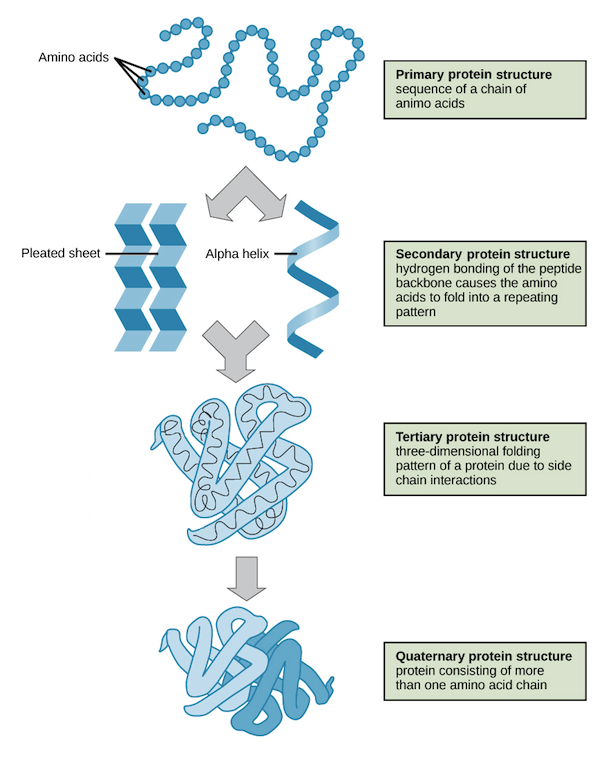
- understanding the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins
- structure and functions of biological catalysts
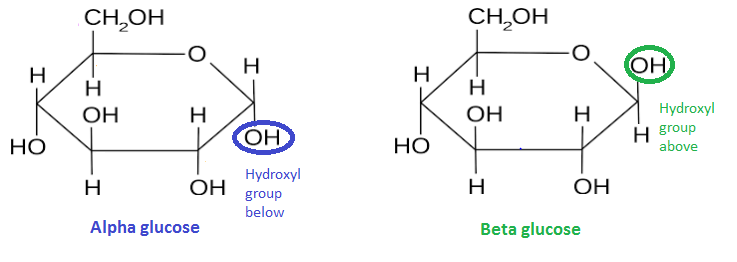
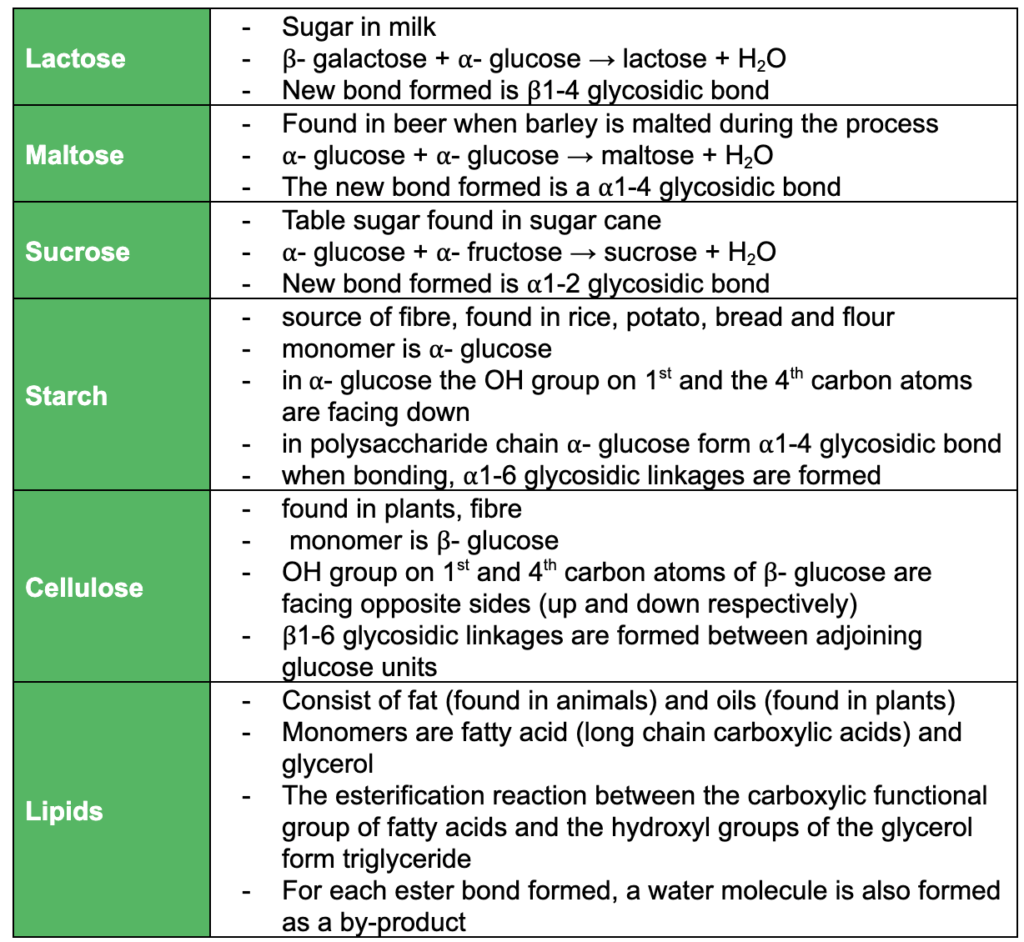
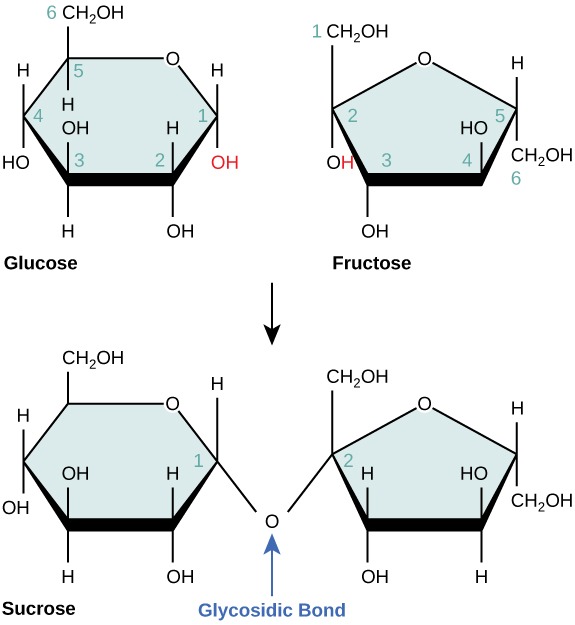
- α-glucose vs β-glucose
- structural properties of starch vs cellulose
- understanding the structure and properties of triglycerides
- saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids
- understanding the process of saponification
- understanding how the structural features of polymers affect their properties
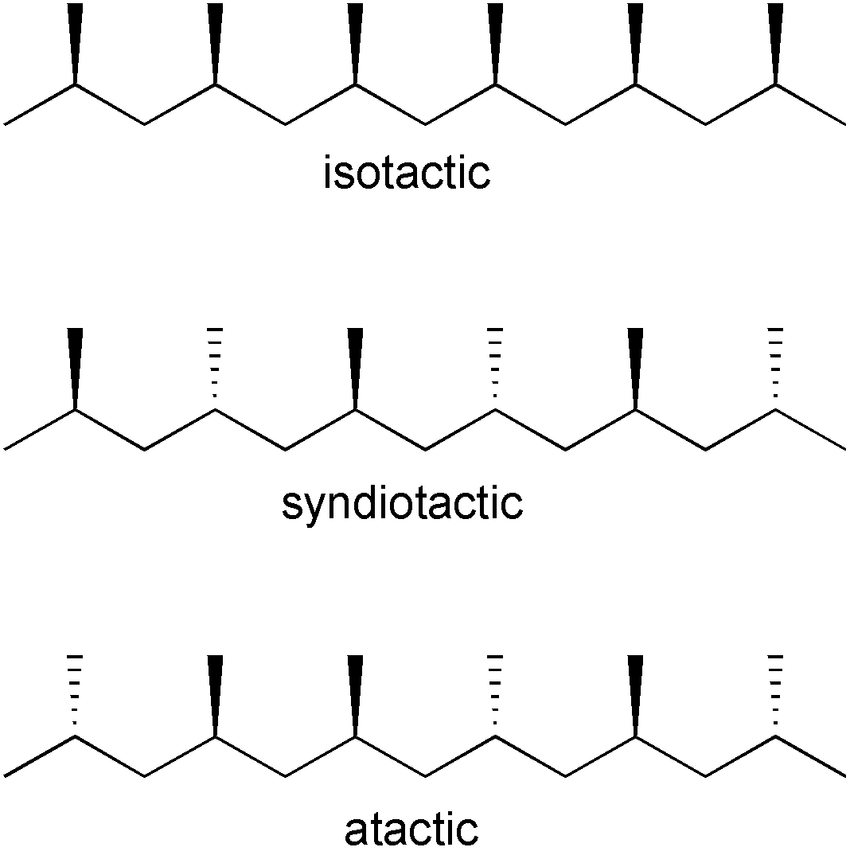
- syntactic vs isotactic vs atactic polymers
Image sourced from Khan Academy
Image sourced from Research Gate
Image sourced from TLAMJS
| Amylose | - Has few glucose units per polymer and is unbranched - Hydrogen bonding forms between sugar units further away gains amylose final shape a coil - Soluble in water |
| Amylopectin | - Has large number of glucose units per polymer bonded by α1-4 glycosidic bonds - It is branched by forming α1-6 glycosidic - Because of its larger size, amylopectin does not dissolve in water and is the water insoluble part of the starch - Hydrogen bonding formed between sugar units |
| Cellulose | - Monomer is a β- glucose which forms β1-4 glycosidic bonds - They form hydrogen bonding with glucose units forms different polymer chains |
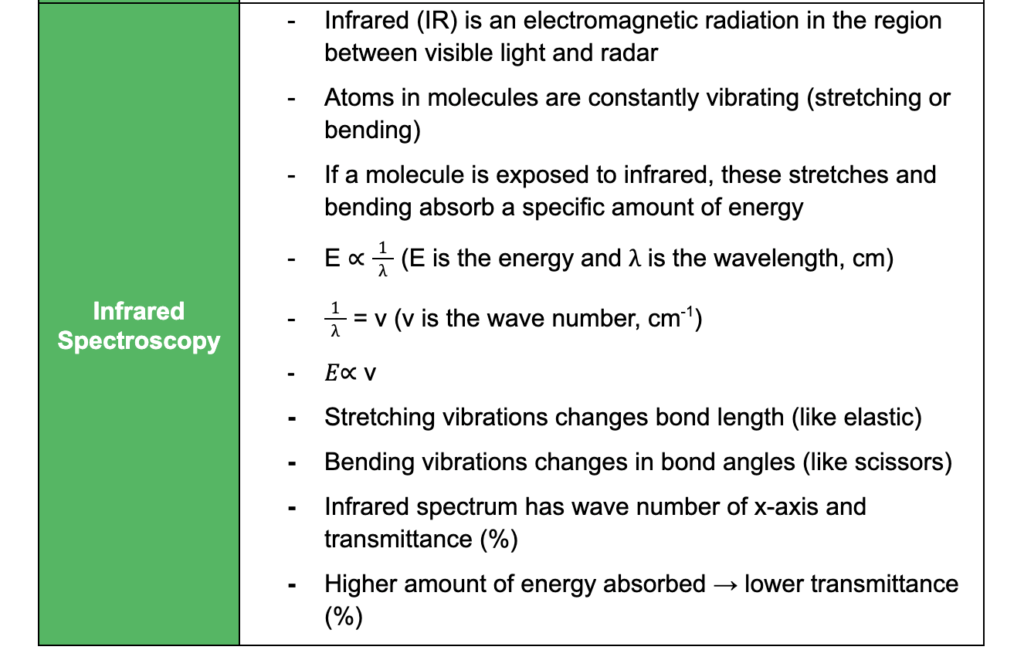
Analytical Techniques
This subtopic covers:
- understanding how proteins can be analysed by chromatography and electrophoresis
Topic 2: Chemical Synthesis and Design
Chemical Synthesis
This subtopic covers:
- understanding the roles of reagents and reaction conditions in chemical synthesis processes including the Haber process, the contact process and the production of biodiesel
- understanding how fuels can be synthesised from a range of chemical reactions
- understanding the role of enzymes in chemical synthesis processes including fermentation to produce ethanol and lipase-catalysed transesterification to produce biodiesel
- describing the production of ethanol from fermentation and the hydration of ethene and the transesterification of triglycerides to produce biodiesel
- understanding the operation of a hydrogen fuel cell under acidic and alkaline conditions
- calculating the yield of chemical synthesis reactions
Green Chemistry
This subtopic covers:
- understanding purpose of the green chemistry principles
- understanding that higher atom economy correlates with a ‘greener’ process
- calculating atom economy to draw conclusions about chemical synthesis processes
Image sourced from Compound Interest
Want to know what the top Chemistry ATAR schools are in Brisbane? Discover the results of our research here!
Macromolecules: Polymers, Proteins and Carbohydrates
This subtopic covers:
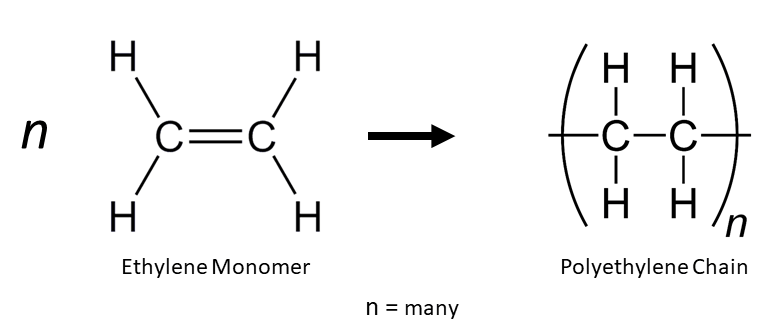
- understanding how addition polymers can be produced from their monomers (e.g. including polyethene, polypropene and polytetrafluorethene)
- understanding how condensation polymers can be produced from their monomers (e.g. polypeptides, polysaccharides and polyesters)
- understanding the advantages and disadvantages of polymer use (e.g. strength, density, lack of reactivity, use of natural resources and biodegradability)
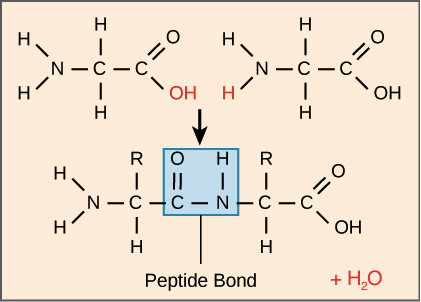
- understanding that polypeptides (proteins) are formed when amino acid monomers are joined by peptide bonds and that that polysaccharides are formed when monosaccharides monomers are joined by glycosidic bonds
- understanding the condensation reaction of monosaccharides to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Image sourced from Syracuse Chemistry of Artifacts Project
Image sourced from Khan Academy
Image sourced from Lumen
Molecular Manufacturing
This subtopic covers:
- understanding that molecular manufacturing processes involve the positioning of molecules to facilitate a specific chemical reaction and the potential to produce specialised products
Also studying Unit 4 of Physics? Check out our Ultimate Guide to Unit 4 Physics: Revolutions in Modern Physics
QCAA Chemistry Unit 4 Assessments
Get ahead in your Unit 4 assessments by understanding where you sit in your cohort compared to your peers with our QCE Cohort Comparison tool!
#1: IA3 – Research Investigation
IA3 is the research investigation. It will assess your ability to create a scientific essay that evaluates a given claim. It constitutes 20% of your overall grade. To find out how to write your research investigation, see The Ultimate Guide to Conducting a QCAA Chemistry Research Investigation So You Can Maximise Marks.
#2: EA – External Assessment
It is an exam that consists of both Unit 3 and 4 content and constitutes 50% of your overall grade. To find out how to best prepare for the external assessment, see How to Ace Your External Assessment for QCAA Chemistry.
For practice questions, see:
Tips for Study
#1: Create a revision table like the one below using the syllabus dot points to guide you
Learn more about taking effective study notes for Chemistry!
#2: Make it visual!
Use diagrams, flowcharts and other visual forms of displaying information where you can when making your notes — this will help to make things more easy to memorise.
#3: Incorporate examples
Include examples of each concept you learn about. For example, if you’re learning about buffer solutions, make sure to include examples of a few relevant buffer solutions!
#4: Time management is essential
The syllabus has a guide on how much time should be spent on each subtopic.
While this guide is technically for teachers and their lesson planning, you as a student can also use it to help guide your study (i.e. to figure out which topics may be more important and therefore require more study time).
Check out also our guide on how to ace Unit 4 of Maths Methods: Further Functions and Statistics!
Are you looking for some extra help with revising QCAA Chemistry Unit 4?
We have an incredible team of QLD Chemistry tutors and mentors!
We can help you master the QCAA Chemistry syllabus and ace your upcoming Chemistry assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational QLD tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Yalindi Binduhewa is an Art of Smart tutor based in Queensland and was part of the very first cohort to go through the ATAR system, so she knows exactly how fun and enjoyable it can be. She is currently studying a Bachelor of Medical Imaging (Honours) at QUT and is loving it. When she’s not doing uni-related stuff or tutoring, she’s hanging out with her friends, rewatching a show for the 100th time, or trying out new crafty projects and discovering that she doesn’t have a talent for everything.