Looking for some HSC Biology practice questions to nail Non-infectious Disease and Disorders? You’ve come to the right place!
As we have seen in the previous modules, much of the HSC Biology syllabus has been dedicated to the study and understanding of diseases.
The previous module explored infectious diseases, however in this module we’ll be branching out and dealing with non-infectious diseases and disorders.
If you need a quick recap of HSC Biology Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders before we jump into some practice questions, make sure you check out our guide here!
Now, let’s get into the nitty gritty of the module and test our knowledge with these HSC style practice questions for Non-infectious Disease and Disorders!
Homeostasis
Causes and Effects
Epidemiology
Prevention
Homeostasis
Inquiry Question 1: How is an organism’s internal environment maintained in response to a changing external environment?
Question 1
Which statement defines homeostasis in multicellular organisms? (1 mark)
a) Homeostasis is the process by which cells maintain their internal environment.
b) Homeostasis is the maintenance of the internal and external environment of the organism.
c) Homeostasis is the process by which animals and plants maintain their body temperature.
d) Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment of the organism.
Sourced from 2004 HSC Biology Question 9
(Investigate the various mechanisms used by organisms to maintain their internal environment within tolerance limits)
Question 2
Homeostatic maintenance of body temperature is an example of: (1 mark)
a) Positive feedback loop
b) Negative feedback loop
c) Stress response
d) Physiological adaptation
(Construct and interpret negative feedback loops that show homeostasis by using a range of sources, including but not limited to: temperature, glucose)
Question 3
Current theories describe differences in the movement of substances through plants. Compare the movement of substances in xylem and phloem tissues. (3 marks)
(Investigate the various mechanisms used by organisms to maintain their internal environment within tolerance limits, including: mechanisms in plants that allow water balance to be maintained)
Sourced from the 2004 HSC Biology Exam Paper
Question 4
Identify an endotherm and explain how their physiological and behavioural responses allow them to maintain their internal environment. (3 marks)
(Investigate the various mechanisms used by organisms to maintain their internal environment within tolerance limits, including: trends and patterns in behavioural, structural and physiological adaptations in endotherms that assist in maintaining homeostasis )
Question 5
Glucose is a chemical in the body which is usually maintained at 5mM (5 millimoles/L) within a normal human body.
a) Explain how the body is able to maintain a near constant level of glucose concentration in the body. (2 marks)
b) On the graph below, sketch the predicted glucose concentration response of an individual who has just consumed a sugary energy drink. On the same graph, sketch the predicted glucose concentration of an individual with diabetes who has just consumed a sugary energy drink. (2 marks)
(Construct and interpret negative feedback loops that show homeostasis by using a range of sources, including but not limited to: temperature, glucose)
Causes and Effects
Inquiry Question 2: Do non-infectious diseases cause more deaths than infectious diseases?
Question 6
How can the study of epidemiology contribute to the fight against disease? (1 mark)
a) By helping reveal mechanisms of the immune response
b) By identifying vectors of disease
c) By proving that UV light causes skin cancer
d) By helping to establish causative factors by identifying statistical correlations
(Analyse patterns of non-infectious diseases in populations, including their incidence and prevalence, including but not limited to)
Question 7
A person with a deficiency in _____________ may develop scurvy, a nutritional deficiency disease. (1 mark)
a) Vitamin C
b) Vitamin D
c) Glucose
d) Insulin
(Analyse patterns of non-infectious diseases in populations, including their incidence and prevalence, including but not limited to nutritional diseases)
Question 8
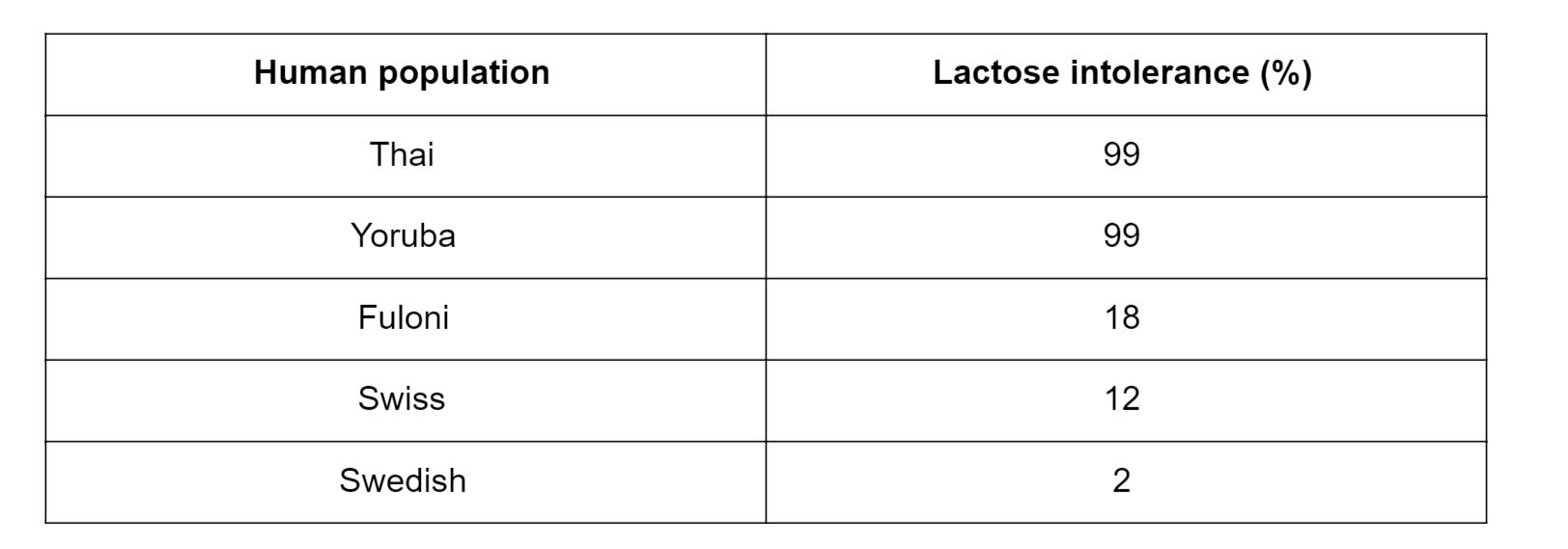
Lactose intolerance is a non-infectious disease found in some humans who cannot digest milk. The causes of noninfectious disease are grouped into three categories. An epidemiological study was undertaken to investigate the cause of lactose intolerance. The study found variation in the occurrence of lactose intolerance in human populations from different parts of the world. Some of the data are shown in the table.
Using information from the table, outline how the study could be continued to determine the cause of the disease. (4 marks)
(Investigate the treatment/management, and possible future directions for further research, of a non-infectious disease using an example from one of the non-infectious diseases categories listed above)
Question 9
A scientist performed an epidemiological study to investigate the cause and effect relationship of smoking and lung cancer as follows
From the information provided, assess the suitability of the methodology for this investigation. (5 marks)
(Evaluate the method used in an example of an epidemiological study)
Sourced from the 2019 HSC Biology additional sample exam questions
Question 10
a) Identify a non-infectious disease caused primarily by environmental exposure. (1 mark)
b) Describe how this non-infectious disease can be treated or managed. (2 marks)
(Analyse patterns of non-infectious diseases in populations, including their incidence and prevalence, including but not limited to: nutritional diseases, diseases caused by environmental exposure)
Epidemiology
Inquiry Question 3: Why are epidemiological studies used?
Question 11
Which of the following terms can be interchangeable with ‘non-infectious disease’? (1 mark)
a) Non-lethal disease
b) Non-communicable disease
c) Non-genetic disease
d) Communicable disease
(Investigate the causes and effects of non-infectious diseases in humans)
Question 12
Epidemiologists are most interested in the study of: (1 mark)
a) Skin diseases
b) The causes of disease, their prevalence and prevention
c) Specifically non-infectious diseases
d) The response of the body to disease
(Investigate the causes and effects of non-infectious diseases in humans)
Question 13
Identify a specific nutritional disease. Describe its cause, symptoms and effects and methods of treatment in the table below. (5 marks)
(Collect and represent data to show the incidence, prevalence and mortality rates of non-infectious diseases, for example: nutritional diseases, diseases caused by environmental exposure)
Prevention
Inquiry Question 4: How can non-infectious diseases be prevented?
Question 14
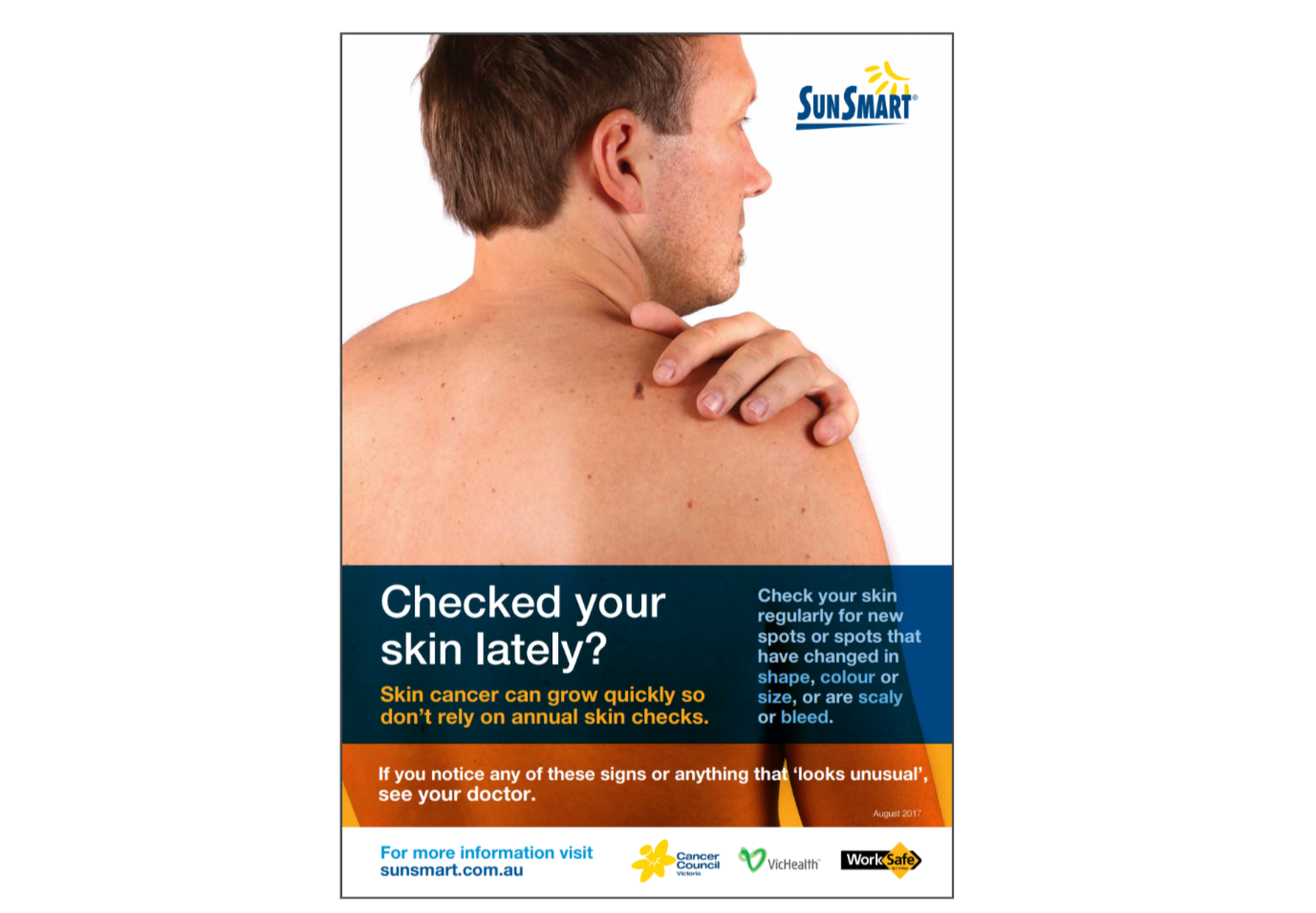
Evaluate the effectiveness of this poster in the prevention of skin cancer. (4 marks)
Image sourced from Sun Smart
(Use secondary sources to evaluate the effectiveness of current disease-prevention methods and
Question 15
Throughout the history of mankind, there have been many non-infectious diseases which have had massive impacts on the world. Using a specific example, explain how educational programs or campaigns were effective in developing strategies to prevent the disease. (3 marks)
(Use secondary sources to evaluate the effectiveness of current disease-prevention methods and develop strategies for the prevention of a non-infectious disease, including but not limited to: educational programs and campaigns, genetic engineering)
Question 16
As blood is filtered through the kidneys, its chemical composition changes. Which of the following chemicals in the blood would drop in concentration as a result? (1 mark)
a) Carbonate ions
b) Urea
c) Fatty acids
d) Amino acids
(Explain a range of causes of disorders by investigating the structures and functions of the relevant organs, for example:hearing loss, visual disorders, loss of kidney function)
Question 17
A patient has an inner ear auditory disorder. Using this information, which of the following technologies would most likely be used to assist with this disorder? (1 mark)
a) Hearing aid
b) Cochlear implant
c) Artificial ear drum
d) Bone conduction implant
(Investigate technologies that are used to assist with the effects of a disorder, including but not limited to: hearing loss: cochlear implants, bone conduction implants, hearing aids)
Question 18
A cochlear implant is a technological advancement that has been developed to assist people with hearing difficulties. Briefly describe how a cochlear implant works and evaluate both it’s benefits and limitations. (3 marks)
(evaluate the effectiveness of a technology that is used to manage and assist with the effects of a disorder)
Question 19
By drawing a flowchart, or an annotated diagram, illustrate how a dialysis machine is used to artificially filter blood in an individual with kidney failure. (5 marks)
(Investigate technologies that are used to assist with the effects of a disorder, including but not limited to: hearing loss: cochlear implants, bone conduction implants, hearing aids, visual disorders: spectacles, laser surgery, loss of kidney function: dialysis)
Question 20
LASIK is a surgical procedure in which the cornea is reshaped to better focus light on the retina of the eye.
a) What purpose does the cornea serve in the focusing of light? (2 marks)
b) Explain how LASIK can be used to treat an individual with hyperopia. (3 marks)
(Investigate technologies that are used to assist with the effects of a disorder, including but not limited to: visual disorders: spectacles, laser surgery)
And that wraps up our 20 practice questions for HSC Biology Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders – good luck!
On the hunt for other HSC Biology practice questions aside from Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders?
Check out some other practice questions below:
- 25 HSC Biology Module 5: Heredity Practice Questions
- 20 HSC Biology Module 6: Genetic Change Practice Questions
- 20 Infectious Disease Practice Questions for HSC Biology
Need some extra help with Non-infectious Disease and Disorders?
We have an incredible team of HSC Biology tutors and mentors who are new HSC syllabus experts!
We can help you master the HSC Biology syllabus and ace your upcoming HSC assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or at our state of the art campus in Hornsby!
We’ve supported over 5,000 students over the last 10 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 19%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational HSC English tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Alex Gao is an Art of Smart mentor and blogger who is passionate about teaching students the skills and know-how of high school. Alex has a great interest in the field of Biology, avidly blogging about the topic whilst also aspiring to become a Biomedical Engineer. Alex graduated in 2018 and was listed on the Distinguished Achievers list for Advanced English, Extension 1 English and Biology.