The topic of Genetic Change is new to the HSC Biology syllabus and may feel like uncharted territory to some students, but that’s why it’s important you consolidate your knowledge with some practice questions!
Module 6 brings into focus new and old concepts from fundamental DNA structure to biotechnology and genetic mutation.
Genetic Change explores the ways in which new genotypes can be introduced into the population, including mutation, environmental pressures and induced with biotechnology.
If you need a quick recap before beginning the practice questions, read up on our HSC Biology Module 6: Genetic Change Guide, which sums up this topic perfectly!
You can also get some support with a HSC Biology tutor in Sydney!
In this article, you can find 20 HSC style practice questions across all three inquiry questions to test and revise your knowledge of Genetic Change!
So, what are you waiting for? Get practising!
Mutation
Biotechnology
Genetic Technologies
Mutation
Inquiry question 1: How does mutation introduce new alleles into a population?
Question 1
A nonsense mutation is a mutation which: (1 mark)
a) Swaps an amino acid with another
b) Generates a stop codon in the sequence
c) Adds a codon to an RNA transcript
d) Deletes sections of RNA
(Compare the causes, processes and effects of different types of mutation, including but not limited to: point mutation, chromosomal mutation )
Question 2
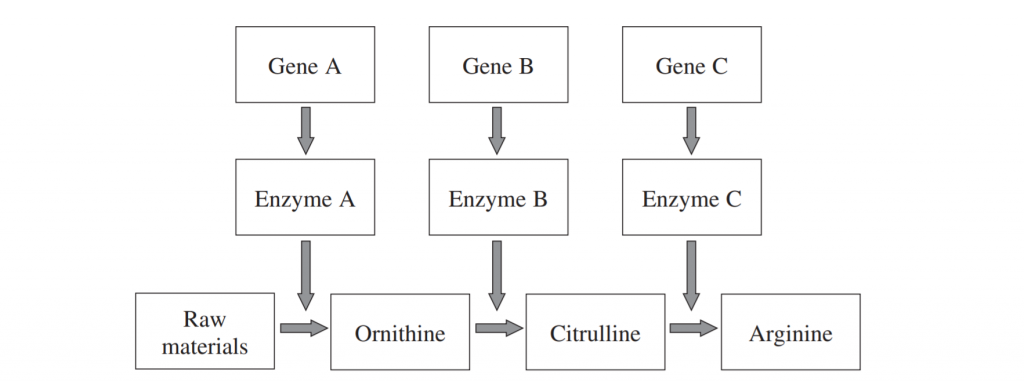
The bread mould, Neurospora crassa, normally produces its own amino acids from raw materials through a system of enzymes.
If a mutation occurred in gene B, the bread mould would still produce arginine if supplied with: (1 mark)
a) Citrulline
b) Ornithine
c) Enzyme C
d) Raw materials
(Sourced from HSC Biology 2019 additional sample HSC questions)
Evaluate the effect of mutation, gene flow and genetic drift on the gene pool of populations
Question 3
Ionizing radiation is a high-energy form of radiation which can cause ions or free radicals to form. Which of the following correctly describes the action that free radicals can have on DNA? (1 mark)
a) Cause oxidative damage from stealing electrons from DNA molecules
b) Release compounds which interfere with transcription processes
c) Cleave DNA strands
d) Prevents DNA polymerase activity
Explain how a range of mutagens operate, including but not limited to: – electromagnetic radiation sources.
Question 4
The flow diagram illustrates the effect of a point mutation on an organism’s genetic sequence.
- CTGAGA → (2) ATGTGA → (3) GACAUC → (4) ?????? → (5) Faulty protein
a) List the sequence of events from stages 2 to 4 that result in the formation of the faulty protein. (3 marks)
b) Describe how a mutagen might cause the changes in the 2nd stage and what consequences this could have for the organism. (4 marks)
Source: Adapted from Biology 2019 additional sample HSC questions
Compare the causes, processes and effects of different types of mutation, including but not limited to: – point mutation)
Question 5
Introns and exons are respectively the non-coding and the coding nucleotide sequences within a gene.
a) Explain what you would expect to happen to the translated DNA sequence if an intron was modified by a mutagen. (3 marks)
b) By the same logic, what would you expect to happen to the translated DNA sequence if an exon was modified by a mutagen. (3 marks)
Assess the significance of ‘coding’ and ‘non-coding’ DNA segments in the process of mutation.
Question 6
Genetic drift is the random process of alleles being passed from parents to offspring. Explain why the process of genetic drift will not increase the genetic diversity of a population. (4 marks)
Evaluate the effect of mutation, gene flow and genetic drift on the gene pool of populations.
Question 7
In the table below, compare the differences in effect between point mutations and chromosomal mutations. (3 marks)
Compare the causes, processes and effects of different types of mutation, including but not limited to: – point mutation – chromosomal mutation
Biotechnology
Inquiry question: How do genetic techniques affect Earth’s biodiversity?
Question 8
In society, there are ideological dilemmas regarding the use of DNA technology. Suggest reasons for this. (3 marks)
Analysing the social implications and ethical uses of biotechnology, including plant and animal examples.
Question 9
Some uses of DNA technology have roused debate over their drawbacks and potential benefits.
a) Name and describe one such use of DNA technology (2 marks)
b) Discuss the reasons behind its support and its opposition (6 marks)
Evaluating the potential benefits for society of research using genetic technologies.
Question 10
Describe TWO potential directions that future use of biotechnology will head towards. (4 marks)
Researching future directions of the use of biotechnology.
Question 11
‘The application of reproductive technologies in plant and animal breeding limits genetic diversity.’ To what extent is this statement correct? (6 marks)
Source: Biology 2019 additional sample HSC questions
Evaluating the changes to the Earth’s biodiversity due to genetic techniques.
Question 12
Identify and describe an early form of biotechnology and how it might have shaped our use of biotechnology today. (5 marks)
Analysing the social implications and ethical uses of biotechnology, including plant and animal examples.
Question 13
Describe some of the uses of biotechnology in the agricultural industry. What are some potential concerns that may arise? (3 marks)
Analysing the social implications and ethical uses of biotechnology, including plant and animal examples
Genetic Technologies
Inquiry question: Does artificial manipulation of DNA have the potential to change populations forever?
Question 14
The insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of an individual who has a genetic disorder to attempt to rectify it, is the fundamental process in which of the following? (1 mark)
a) Selective breeding
b) Gene therapy
c) Hybridisation
d) Cloning
Investigate the uses and advantages of current genetic technologies that induce genetic change
Question 15
Which of the following poses as a disadvantage when utilising artificial, mechanical pollination? (1 mark)
a) Less efficient than natural means
b) More efficient than natural means
c) Largely labour intensive
d) Less expensive than natural means
Compare the processes and outcomes of reproductive technologies, including but not limited to: – artificial insemination – artificial pollination
Question 16
A recombinant DNA molecule is created using: (1 mark)
a) 2 DNA fragments
b) 2 or more DNA fragments
c) 2 or more DNA fragments from different organisms
d) None of the above
Describe techniques and applications used in recombinant DNA technology
Question 17
Using a flowchart, or other diagrammatic methods, show the sequence of events which results in the formation of recombinant DNA. (4 marks)
Source: Adapted from Biology 2019 additional sample HSC questions
Describe techniques and applications used in recombinant DNA technology
Question 18
Selective breeding is a form of biotechnology
a) Explain, using a specific species of animal, what is meant by the term selective breeding. (2 marks)
b) Describe how the biodiversity of the species has changed as a result of selective breeding. (2 marks)
Evaluate the effect on biodiversity of using biotechnology in agriculture
Question 19
Since the mid to late 20th century, the development of genetic technology was centered around benefiting mankind. This resulted in a range of beneficial drugs, vaccines and food crops which were engineered using genetic technology.
Select one example and assess the significance of genetic technology in its creation and implementation. (8 marks)
Evaluate the benefits of using genetic technologies in agricultural, medical and industrial applications
Question 20
Transgenic organisms are often used and cultivated in the agricultural industry. Many of these GMOs are created using recombinant DNA technology. Outline the stages of recombinant DNA technology. (5 marks)
Describe techniques and applications used in recombinant DNA technology
On the hunt for other HSC Biology practice questions aside from Module 6: Genetic Change?
Check out some other practice questions below:
- 25 HSC Biology Module 5: Heredity Practice Questions
- 20 Infectious Disease Practice Questions for HSC Biology
- HSC Biology Practice Questions for Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders
Looking for some extra help with answering HSC Biology Module 6: Genetic Change practice Questions?
We have an incredible team of HSC Biology tutors and mentors who are new HSC syllabus experts!
We can help you master the HSC Biology syllabus and ace your upcoming HSC Biology assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or at our state of the art campus in Hornsby or the Hills!
We’ve supported over 5,000 students over the last 10 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 19%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational HSC Biology tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Alex Gao is an Art of Smart mentor and blogger who is passionate about teaching students the skills and know-how of high school. Alex has a great interest in the field of Biology, avidly blogging about the topic whilst also aspiring to become a Biomedical Engineer. Alex graduated in 2018 and was listed on the Distinguished Achievers list for Advanced English, Extension 1 English and Biology.