One of the core topics of HSC Biology is the study of infectious disease. This module involves unravelling the mysteries behind the cause of disease, how our bodies react to them and how disease can be treated, prevented and controlled.
To help you prepare and revise for Module 7, we’ve curated a selection of sample HSC style questions to consolidate your knowledge.
Don’t forget to check out our break down guide to Module 7: Infectious Disease if you need a quick recap of the module! You can also get some additional support with our Sydney Biology tutors.
Let’s dive in!
Causes of Infectious Disease
Inquiry question: How are diseases transmitted?
Question 1
In terms of infectious disease transmission, which of the following best defines a vector? (1 mark)
a) The process by which a disease is spread
b) An insect which spreads a pathogen
c) A pathogenic virus which spreads a disease
d) Any agent which carries or spreads a pathogen
(Investigate modes of transmission of infectious diseases, including direct contact, indirect contact and vector transmission)
Question 2
Which of the following are examples of pathogens? (1 mark)
a) Vectors, protozoans, bacteria
b) Viruses, prions, bacteria
c) Antigens, fungi, bacteria
d) Parasites, antibodies, protozoans
(Classifying different pathogens that cause disease in plants and animals)
Question 3
Koch contributed to an understanding of a disease by developing: (1 mark)
a) A method to link a particular pathogen to the cause of a disease
b) An experiment that disproved the theory of spontaneous generation
c) A method of killing microbes by heating and thus preventing decay
d) An immunisation program based on a knowledge of immune responses
Sourced from 2010 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate the work of Robert Koch and Louis Pasteur, to explain the causes and transmission of infectious diseases, including: – Koch’s postulates )
Question 4
Evaluate the contributions made by both Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch to our present understanding of the causes and possible prevention of infectious diseases. (8 marks)
Sourced from 2002 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate the work of Robert Koch and Louis Pasteur, to explain the causes and transmission of infectious diseases, including: – Koch’s postulates)
Question 5
With specific reference to an animal disease in Australia, assess the causes and effects of the disease on the agricultural industry. (5 marks)
(Assess the causes and effects of diseases on agricultural production, including but not limited to: – animal disease)
Responses to Pathogens
Inquiry question: How does a plant or animal respond to infection?
Question 6
Which biological term is best described by ‘engulfing and destruction of bacteria or other foreign bodies’? (1 mark)
a) Vaccination
b) Attenuation
c) Phagocytosis
d) Antibody production
Sourced from HSC Biology 2007 Exam
(Analyse responses to the presence of pathogens by assessing the physical and chemical changes that occur in the host animals cells and tissues)
Question 7
Which of the following prevents entry of pathogens into the human body? (1 mark)
a) The skin and phagocytosis
b) The skin and chemical barriers
c) Inflammation response and phagocytosis
d) Inflammation response and chemical barriers
Sourced from HSC Biology 2009 Exam
(Analyse responses to the presence of pathogens by assessing the physical and chemical changes that occur in the host animals cells and tissues)
Question 8
When a foreign body breaches the first line of defence, the mast cells produce histamines in response. What is the role of histamines in the defence of the body?
a) To attack the invading pathogen
b) To activate B and T lymphocytes of the specific immune response
c) To activate the inflammation response and increase blood flow to the affected area
d) To retain information on a pathogen’s antigen so that the immune system can respond quickly to any subsequent infection
(Analyse responses to the presence of pathogens by assessing the physical and chemical changes that occur in the host animals cells and tissues )
Question 9
Identify a viral pathogen affecting Australian plants and outline its biological effects on the plant. (3 marks)
(Investigate the response of a named Australian plant to a named pathogen through practical and/or secondary-sourced investigation, for example: – fungal pathogens – viral pathogens)
Question 10
You undertook a first-hand investigation to examine plants for evidence of pathogens and insect pests.
Use the information you gathered to complete the table. (3 marks)
Sourced from HSC Biology 2004 Exam
(Investigate the response of a named Australian plant to a named pathogen through practical and/or secondary-sourced investigation, for example: – fungal pathogens – viral pathogens)
Immunity
Inquiry question: How does the human immune system respond to exposure to a pathogen?
Question 11
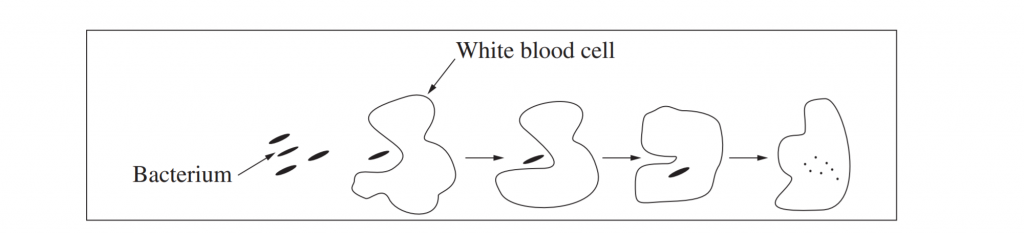
The diagram below illustrates one process that occurs as part of an immune response. What process does the diagram illustrate? (1 mark)
a) Cytokinesis
b) Inflammation
c) Osmosis
d) Phagocytosis
Sourced from 2004 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate and model the innate and adaptive immune systems in the human body)
Question 12
What is the function of T-helper cells? (1 mark)
a) Initiation of inflammation
b) Phagocytosis of bacteria and viruses
c) Promotion of B-cell and T-cell activity
d) Production of specific antibodies against pathogens
Sourced from 2003 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate and model the innate and adaptive immune systems in the human body)
Question 13
Humoral immunity is a form of adaptive immunity. It is characterised by the flow of which of the following in the blood? (1mark)
a) Macrophages
b) Antigens
c) Antibodies
d) Cytotoxic t cells
(Explain how the immune system responds after primary exposure to a pathogen, including innate and acquired immunity)
Question 14
a) Identify ONE type of T lymphocyte. (1 mark)
b) Distinguish between the function of a B cell and a T cell. (2 marks)
Sourced from 2004 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate and model the innate and adaptive immune systems in the human body)
Question 15
a) Outline the 3 key differences between innate immunity and adaptive immunity. (3 marks)
b) The principle of vaccinations is to introduce your body to attenuated or inactivated pathogens to confer immunity to the individual. Which system of immunity does this process mainly make use of? (1 mark)
(Investigate and model the innate and adaptive immune systems in the human body)
Prevention, Treatment and Control
Inquiry question: How can the spread of infectious diseases be controlled?
Question 16
Overseas avian enthusiasts brought their hawks to Australia for an international hawking competition. The birds were kept in quarantine for a duration of time before the event began. In terms of biosecurity what is the reason for this process? (1 mark)
a) To acclimatise them to Australian conditions
b) To make sure no bird diseases spread to spectators
c) To make sure the birds don’t contract Australian diseases
d) To make sure the birds do not have an infectious disease
(Investigate procedures that can be employed to prevent the spread of disease)
Question 17
How do vaccinations prevent disease? (1 mark)
a) They increase the inflammation response
b) They enable infected cells to seal off the pathogen
c) They increase the number of antibodies against the pathogen
d) They decrease the number of antigens that trigger the immune response
Sourced from NESA HSC Biology additional sample examination questions
(Investigate procedures that can be employed to prevent the spread of disease)
Question 18
Antibiotics are a widely used drug in most developed countries. They are frequently used to treat bacterial infections and are sometimes added to animal feed.
Explain how the widespread use of antibiotics can impact the spread of disease in the future. (4 marks)
(Investigate and assess the effectiveness of pharmaceuticals as treatment strategies for the control of infectious disease)
Question 19
Lifetime traceable tags as shown in the diagram are now required on all cattle in Australia.
Discuss the use of this strategy in dealing with diseases. (4 marks)
Sourced from 2005 HSC Biology Exam
(Investigate procedures that can be employed to prevent the spread of disease)
Question 20
Assess the importance of the confiscation or destruction of high risk imported goods to Australian biosecurity and its effects on preventing disease. (6 marks)
(Investigate and evaluate environmental management and quarantine methods used to control an epidemic or pandemic)
And that wraps up our 20 practice questions for HSC Biology Module 7: Infectious Disease – good luck!
On the hunt for other HSC Biology practice questions aside from Module 7: Infectious Disease?
Check out some other practice questions below:
- 25 HSC Biology Module 5: Heredity Practice Questions
- 20 HSC Biology Module 6: Genetic Change Practice Questions
- HSC Biology Practice Questions for Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders
Looking for some extra help with HSC Biology Infectious Disease?
We have an incredible team of HSC Biology tutors and mentors who are new HSC syllabus experts!
We can help you master the HSC Biology syllabus and ace your upcoming HSC Biology assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or at our state of the art campus in Hornsby!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational HSC Biology tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Alex Gao is an Art of Smart mentor and blogger who is passionate about teaching students the skills and know-how of high school. Alex has a great interest in the field of Biology, avidly blogging about the topic whilst also aspiring to become a Biomedical Engineer. Alex graduated in 2018 and was listed on the Distinguished Achievers list for Advanced English, Extension 1 English and Biology.