Are you studying Shakespeare’s ‘Othello’ and are struggling to understand his writing, the themes and crafting an essay for your upcoming assessment? We’re here to help you with a simple summary of Othello, its key characters and context so you can formulate your own analysis!
PLUS, you’ll be getting a step-by-step analysis table (called a TEE Table) as well as a sample paragraph so you can see what an extensive response looks like.
So, let’s get into it and ace your essay on Othello!
Summary of Othello
Key Characters in Othello
Context
Themes Explored in Othello
Essay Analysis of Othello
Summary of Othello
Othello is one of Shakespeare’s greatest tragedies, performed in five acts depicting the dramatic downfall of a hero as a result of racial prejudice, jealousy and pride.
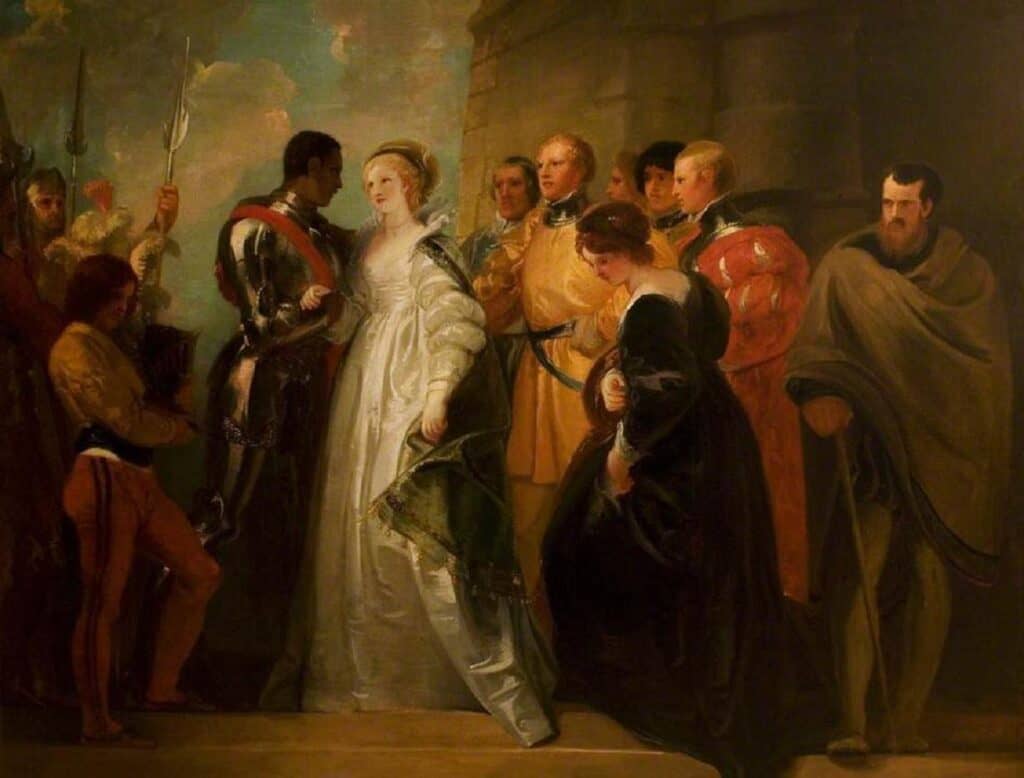
The play is set in motion when an African General in the Venetian Army, Othello, passes over Iago, a senior officer in the Venetian Army who is under Othello’s command, to promote Michael Cassio as his chief lieutenant instead.
Driven by extreme hate and jealousy of Othello’s celebrated successes and his need for control, Iago is determined to destroy Othello and begins to plot Othello’s undoing through his wife, Desdemona, the daughter of an important Venetian senator, Brabantio.
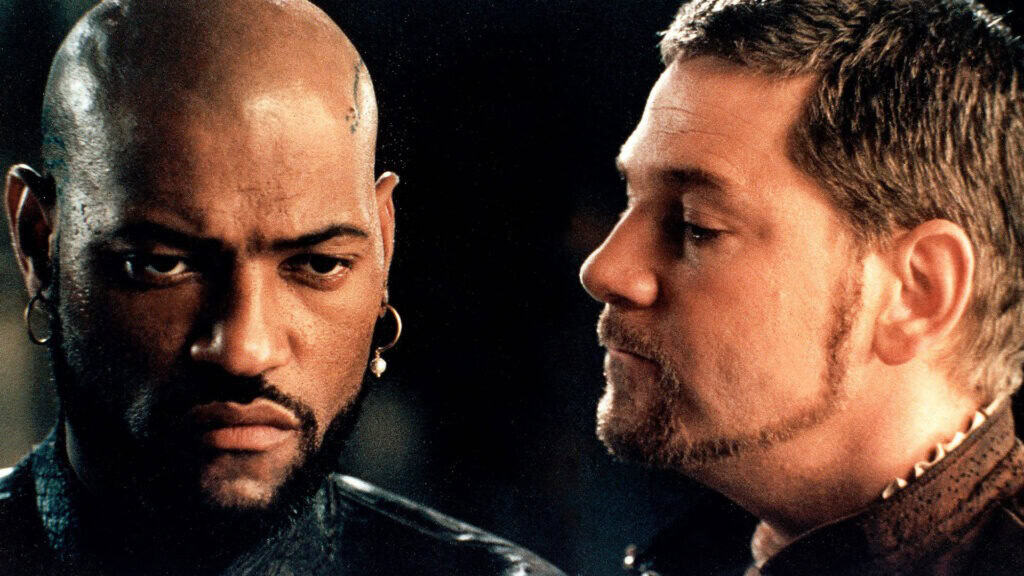
Laurence Fishburne and Kenneth Brannagh as Othello and Iago in Oliver Parker’s 1995 ‘Othello’
Act 1
Iago firstly enlists Roderigo, Desdemona’s rejected lover, to inform Brabantio about Desdemona’s elopement to Othello, urging an enraged Brabantio to appeal to the Duke of Venice to have Othello punished for seducing Desdemona by witchcraft. However, Othello defends himself in front of Brabantio and his senators, Desdemona confirms that she is deeply in love with Othello, and that their marriage was not coerced.
Brabantio warns Othello that Desdemona will betray him, and says, “Look to her, Moor, if thou hast eyes to see. She has deceived her father, and may thee,” to which Iago takes note as they leave Venice for Cyprus.
Act 2
After arriving in Cyprus and learning that the storm has destroyed the Turkish fleet, Othello commences a celebration with his army, while he leaves to consummate his marriage to Desdemona. Iago gets Cassio drunk, and persuades Roderigo to duel Cassio.
Montano tries to calm them down, but an inebriated Cassio proceeds to fight, injuring Montano in the process. Othello reappears, questions the men and blames Cassio for the feud, thus stripping him off his rank.
Cassio is distraught, however, Iago convinces him to plead to Desdemona to have Othello reinstate him. She succeeds.
Act 3
Iago begins to convince Othello of a false affair between Cassio and Desdemona. When Desdemona drops her handkerchief, Othello’s first gift to her, Emilia (Iago’s wife) gives it to Iago, unaware of his plans.
Persuaded by Iago’s false claims and planting seeds of doubt, Othello swears Desdemona and Cassio’s death, and promotes Iago as his lieutenant.
Act 4
Iago then plants Desdemona’s handkerchief in Cassio’s belongings, while ordering Othello to watch Cassio’s responses as Iago questions him from afar. While Iago questions Cassio about his affair with Bianca, a local courtesan, Othello is made to believe that the two men are talking about Desdemona.
Meanwhile, Bianca appears and accuses Cassio of gifting her with a second-hand item. Othello, still watching from afar, is enraged, and believes Iago’s claims that Desdemona had given this handkerchief to Cassio.
A hurt Othello resolves to kill Desdemona and Cassio with Iago’s help, and strikes Desdemona in front of visiting Venetian nobles. Roderigo, still upset, is urged by Iago to kill Cassio.
Act 5
Roderigo pursues Cassio in the streets, and Cassio injures Roderigo. Meanwhile, Iago appears from the shadows and stabs Cassio from behind, wounding his leg.
In the night, Iago manages to hide his identity, and joins Lodovico and Gratiano when Cassio cries for help, thus appearing as unknowing of the scuffle. When Cassio identifies Roderigo as the attacker, Iago stabs him to prevent him from revealing the plan.
Othello confronts Desdemona, and smothers her with a pillow. Emilia arrives, calling for help, to which the former governor Montano arrive with Gratiano and Iago. After Othello shows proof of the handkerchief, Emilia realises Iago’s plot and exposes him, whereupon he kills her.
Meanwhile, Othello realises Desdemona’s innocence and stabs Iago in revenge. Iago refuses to explain his motives and Lodovico apprehends Iago and Othello for the murders of both the women, but Othello commits suicide. Cassio arrives and is promoted as Othello’s successor, and punishes Iago justly.
Key Characters in Othello
Othello
As a competent and highly regarded serviceman of the Venetian Republic, Othello is the ‘Moorish’ General of the Venetian Army and the protagonist of our story. He elopes with Desdemona, and ultimately succumbs to Iago’s deceit, leading to his tragic death.
The audience follows Othello’s eventual downfall through the collapse of his own self-perception, as instigated and dominantly narrated by Iago. It is through Iago that the audience sees Othello’s eroding sense of self, calculating his moves to remind Othello that he is the ‘Moor’ and signifying his difference.
Here, Othello’s own fears of himself of his age, his status and his race come to light, especially the fear of Desdemona’s infidelity which immediately leads him to farewell his soldierly career.
He is referred to as “an old black ram” in comparison to Desdemona’s nature as a “white ewe” (I.i.88), ostracising him from the rest of society and thus making him an easy prey for Iago. Until the very late stages of the play, Othello’s agency is not singular, but instead is driven by Iago.
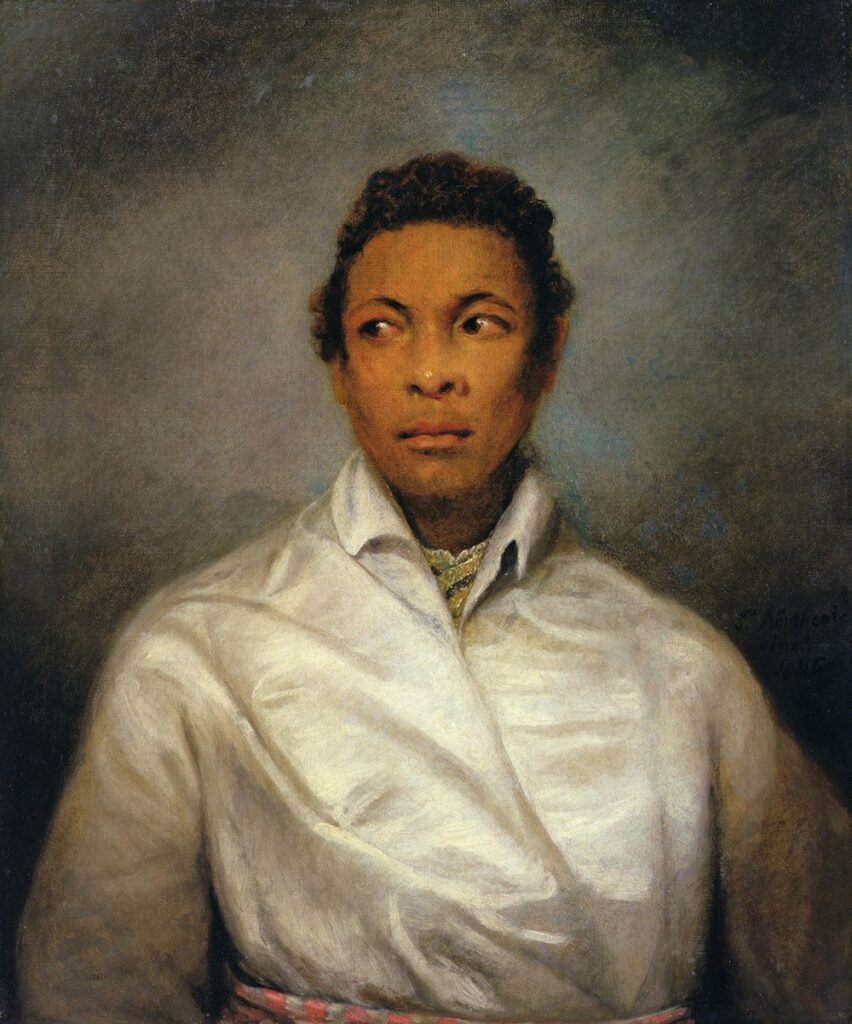
A Moor by James Northcote (1826) – Ira Alridge as the first Black actor in Britain to play Othello
Sourced from Manchester Art Gallery
However, Othello also positions himself as an outsider, which adds to his victimisation. Though Othello’s skill as a soldier and leader positions him as a great influence, it is still his exotic qualities that entice others such as Desdemona and Brabantio to him.
As an eloquent speaker, the Duke mentions that ‘I think this tale would win my daughter too’ (I.iii.70). These qualities present him as an outsider, both in race and in eloquence, thus creating a cathartic ending for a hero falling prey to tragedy.
Iago
It is clear that Iago’s extreme jealousy and need to avenge Othello’s ‘wrongdoing’ engineers the plot for revenge. Here, Iago’s malicious intentions cultivate the entire scenario of revenge in the play, and thus, he is widely regarded as a ‘Machiavellian’ character (from Machiavelli’s 1532 political treatise The Prince).
He is cunning, cold, and concerned with personal gain over morality.
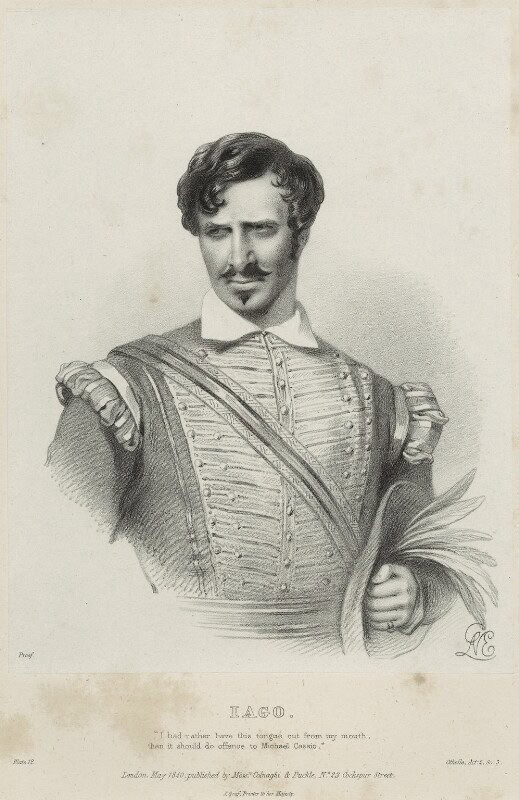
Charles Kemble as Iago in Othello, by Richard James Lane (1840)
Sourced from National Portrait Gallery, London
Iago cleverly distorts Othello’s reality of himself and the reality for the rest of the characters, creating an ambiguous and distrustful narrative that culminates in destruction.
Firstly, Iago’s jealousy stems from his hatred for Othello’s success as an outsider in Venice. Othello occupies a difficult position and becomes the most fated soldier, despite his appearance in a European city. This charges Iago’s animalistic language towards Othello, regarding him as a ‘Barbary horse’ (1.i.113).
Secondly, he resents Cassio’s rise to power (1.iii). Possessing an extraordinary power to manipulate, Iago’s jealousy acts as a catalyst to create a cycle of revenge and envy that loops in Othello and Roderigo to destruction.
Context of Othello
The earliest recorded performance of Othello was in 1604, under the title The Moor of Venice, during the cusps of the reigns of Elizabeth I and James I. Othello’s Mediterranean setting is significant as it presents an age of increasing European maritime power, and authority over the ocean was crucial for the politics in Mediterranean states.
This involved both Western powers (Spain, Portugal and Italy) as well as the Eastern Mediterranean empire of the Ottomans (modern day Turkey), who were in constant conflict over control of the Adriatic and eastern Mediterranean seas.
While the first part of the play is set in Europe, Act II of the play is set in the small island of Cyprus, the site of Venetian and Ottoman rivalries. After the death of James II, Venice had full control of Cyprus, which proved strategic for Venetian Army to launch attacks against the Ottomans. Othello’s military successes are set within this conflict.
Othello’s Castle, North Cyprus
Sourced from Visit North Cyprus
Othello’s life story also reflects the mobility (including enforced) of lives across the Mediterranean. Othello is referred to as a ‘Moor’, signifying his racial difference from the rest of the — mostly white — European characters.
However, there is no clear concept of ‘Moor’, as the term can refer to an Arabian person from North Africa or a Southern Spanish person. This term is used today in quotations.
Though Othello’s race bridges the gap between his military service and war against the Muslim empire, Othello nevertheless succumbs to Iago’s words, increasingly becoming vulnerable about his status and heightening his insecurities. Iago plays on the cultural divide between black-and-white, ultimately fuelling Othello’s anxiety and the downfall of his status and his marriage.
Themes Explored in Othello
Below are some key ideas from Othello. These are great starting points for you to consider your arguments, thesis and topic sentences:
- Racial Prejudice
- Jealousy and revenge
- Deception — appearance VS reality
Racial Prejudice
The role of racial prejudice is imperative in Iago’s emotional and mental poisoning of Othello, driving him to the point of distrust and extreme isolation. Other characters already hold Desdemona and Othello’s marriage in disdain, such as Brabantio who warns that “Bond-slaves and pagans shall our statesman be” (1.i.98-99), putting them against the status quo and the present view of their world.
Iago only exacerbates Othello’s ingrained fears of ‘Moorish’ differences towards his position in the Army, his wife and his status in Venice, becoming a lethal weapon in Othello’s self-destruction.
This drives him to the point of isolation and self-hatred, where he trusts no one but Iago. Eventually, Othello begins to blame his complexion for allegedly depriving his wife of her good nature: ‘Her name, that was as fresh / As Dian’s visage, is now begrim’d and black / As mine own face’ (3.ii.386-8).
His inherent fears of his Moorish complexity and exotic characteristics tainting his wife consequently prompts his vulnerability towards his marriage, and his lack of self-reassurance unconsciously places him in a white perspective of his own blackness. Therefore, these ingrained perspectives of himself in society seal both the fates of himself and of Desdemona.
Jealousy and Revenge
Iago’s jealousy drives him to deadly extremes to emotionally violate his alleged ‘oppressors’, and provokes the rest of his characters such as Roderigo, Bianca and Othello into ‘the green-eyed monster’ (3.iii.166).
Roderigo’s unrequited love for Desdemona makes him extremely jealous of Othello, and Bianca is jealous when she finds Desdemona’s handkerchief in Cassio’s lodgings. Iago provokes this jealousy on Othello with the handkerchief as ‘ocular proof’ (3.iii.360) of the infidelity, which has been passed from Desdemona, to Emilia and then to Bianca, drawing an implicit parallel between the innocent women and the men’s perception of women in marriage.
This consumes Othello the most, in which Iago’s extreme need for revenge fuels the strategically distorted narrative, confirms his suspicions and fulfils his expectations.
Deception — Appearance VS Reality
Iago’s power to manipulate allows him to plant seeds of doubt in Othello and other characters throughout the play. His success to quickly and cleverly manipulate Othello stems from the tales of perceived misogyny and view of female sexuality that is already shared among men.
Iago reminds Othello that Desdemona is a creature of deception, as she ‘did deceive her father, marrying you’ (3.iii.206), and that she will do so to him: ‘Look to her, Moor, if thou hast eyes to see; / She has deceived her father, and may thee’ (1.iii.292-3).
Dramatic irony (the gap of knowledge between what the audience and the character knows) serves as a catharsis for the audience and provokes an emotional response in the tragedy. Here, Iago continues to finely calibrate a sense of torment in Othello’s imagination through his deceptive language as he tells Othello that Cassio lies ‘with [Desdemona], on her, as you will’ (4.i).
In doing so, he constantly plants mental images of uncertainty and instability in Othello, leaving Othello to connect and unknowingly create a flawed narrative that he believes to be true. Iago masks this deception as he merely justifies his actions by reflecting his victim’s own beliefs: ‘I told him what I thought and no more / Than what he found himself was apt and true’ (5.ii.176-77).
In this way, he deflects blame from himself, and while he engineers the chaos, he does not become the fundamental source of Othello’s, Desdemona’s and Emilia’s deaths.
Studying on the night before your exam? Make sure to use our exam prep routine for English here!
Essay Analysis: How to Analyse Othello in 3 Steps
Most students will begin to write their essay and their thesis without any supporting evidence, themes or analysis. You will need to equip yourself with the knowledge of your text before answering anything about it.
Analysing a text, providing it with evidence and techniques may be easier than you think… it’s like a formula! We can say ‘a + b = c’. But what are these?
A = Evidence
B = Technique
C = Analysis
After knowing your text, you can build ideas from it, and start writing your thesis! So, let’s walk through on how to analyse Othello:
Step 1: Choosing your evidence (‘A’)
Choosing your evidence can be tough, because there are just so many good ones you can choose from!
But you need to remember that you must choose evidence that supports your argument and answers the question. But how do we do that?
Let’s gather important pieces that we have seen throughout this article. Here is one we have chosen for you:
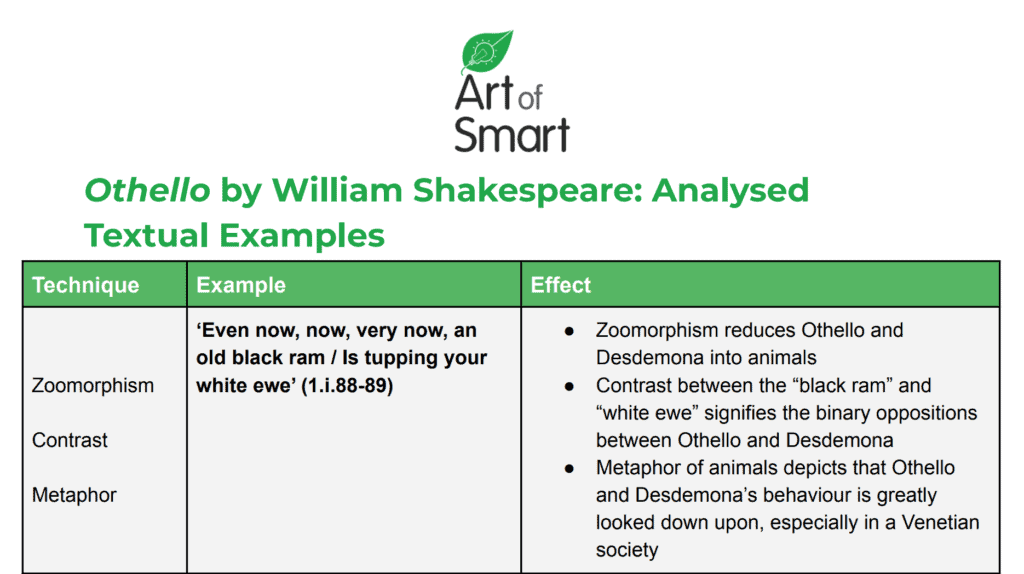
‘Even now, now, very now, an old black ram / Is tupping your white ewe’ (1.i.88-89)
Step 2: Identifying your technique(s) (‘B’)
This isn’t just about finding any old technique or using a technique that is fancy and hoping for the best! It’s about what best suits your evidence, your analysis, and subsequently, your answer to the question.
Techniques are what help composers convey the message to their audience and their readers. So, we need to identify a technique that will enable you to say something about your idea that’s interesting, and will contribute to your analysis of Othello.
Try to focus on finding examples with techniques which unveil a deeper meaning like metaphors, similes, figurative language, connotations, symbolism and recurring motifs. Other techniques like alliteration and repetition are a bit harder to find a deeper meaning in!
We have identified 3 techniques in the quote above: zoomorphism, contrast and metaphor.
It’s always great to try and find multiple techniques in your quotes as it allows you to take your analysis up a notch!
Step 3: Writing your analysis (‘C’)
When you write the analysis for your essay on Othello, it is important to always focus on what the effect of the technique is. One of the worst things you can do when writing analysis is technique labelling. Technique labelling would look like this:
The zoomorphism between “black ram… tupping [your] white ewe” shows how Iago wants Brabantio to see Othello’s elopement to Desdemona, contrasting his physical appearance and nature to hers.
Instead, we need to flesh out how those techniques get us to our point. Firstly, Iago’s language is important as he uses zoomorphism to reduce Othello and Desdemona into animals.
Secondly, the contrast between the “black ram” and “white ewe” is important to signify the binary oppositions between Othello and Desdemona.
Lastly, the use of the metaphor of animals is important as it depicts that Othello and Desdemona’s behaviour is greatly looked down upon, especially in a Venetian society.
So, if we include that in our essay analysis of Othello, this would look like…
Iago’s cries to Brabantio that “Even now, now, very now, an old black ram / Is tupping your white ewe” (1.i.88-89), using zoomorphism to reduce Othello and Desdemona’s wildly radical behaviour into animals. The contrast between the “black ram” and the “white ewe” signifies the binary oppositions between Othello and Desdemona, and is a metaphor for their disapproved marriage against social norms and the racial prejudice pervading their Venetian society.
Need some help with your essay analysis of other texts aside from Othello?
Check out other texts we’ve created guides for below:
- Romeo and Juliet
- Run Lola Run
- King Lear
- Jane Eyre
- The Great Gatsby
- Persepolis
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- The Book Thief
- The Tempest
- Blade Runner
- Things Fall Apart
- Mrs Dalloway
We’ve also got articles specifically on plays by Shakespeare which you can have a read through below:
- Macbeth
- King Richard III
- A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Hamlet
- The Merchant of Venice
- Much Ado About Nothing
- Romeo and Juliet
- The Tempest
Are you looking for some extra help with your essay analysis of Othello?
We have an incredible team of tutors and mentors!
We can help you master your essay analysis of Othello by taking you through the summary, context, key characters and themes. We’ll also help you ace your upcoming English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years, and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Camille Chin is your certified Art of Smart Veteran! Starting as a student at Art of Smart herself, she felt passionate about helping students boost their academic confidence so that they can achieve and reach their full potential in their studies. She currently studies Law and Arts – English at Macquarie University, and loves volunteer firefighting, reading and watching musical theatre in her spare time.