You’re going to love the new changes to the Year 11 Biology Module 3: Biological Diversity syllabus!
In the previous modules, you may have gone through what kind of features cells have and their relationship to other cells (in both single and multicellular organisms).
Biological Diversity and the next module Ecosystem Dynamics explore an organism’s relationship to its environment. Think of it like zooming out to see the big picture!
There are new outcomes in this new syllabus which means you get to spend more time understanding key concepts. There is also a focus on using secondary sources (as you can imagine, looking at evolution first hand can get pretty hard).
Changes to Year 11 Biology Module 3: Biological Diversity
Topics Covered in Year 11 Biology Module 3
How do I get a Band 6 in Year 11 Biology Module 3: Biological Diversity?
Let’s get into Biological Diversity!
What’s stayed the same?
Skills relevant to ‘working scientifically’ haven’t changed since the last syllabus. These include designing questions and hypotheses and conducting investigations. You also still have to go out and do fieldwork!
So, what changed?
A big part of science is asking questions, which is why we have inquiry questions. They are overarching questions that address the main issue that a specific dot point wants to teach you. Below, we will go through what those inquiry questions are asking of you!
The new syllabus has also updated content to include new findings in biology. These include:
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples, paleontological and geological evidence of past changes in ecosystems
You might be asking how you are going to learn things in greater depth. As the name suggests, you are going to be doing depth studies. These are ‘practical investigations, fieldwork, data analysis, secondary sourced investigations’.
Scientific investigations like to follow the cycle of: question à investigation à data analysis à problem solving à communication. You are now able to show your competence and creativity by experiencing this process yourself like real scientists!
Why did they do this?
NESA has condensed information for you in a way that is more focused, easy to understand and categorised. This is great news because it means you have more time to learn same concepts as the previous syllabus (and more!!).
This new syllabus not only tests your knowledge, but other skills like your analytical and problem-solving skills. Biology isn’t just about what you know! This is a great opportunity to show your strengths in finding information, asking questions and investigating issues using current knowledge.
Now that we’ve gone through the changes, let’s take a closer look at Biological Diversity in terms of what you’ll be going through.
Breaking Down Biological Diversity
This syllabus follows this question > investigation > data analysis > problem solving > communication flow in the context of:
- What kind of diversity exists
- How these changes in organisms came to be
- The theory of evolution
- Real life examples of diversity
The concepts of diversity and evolution are interconnected because the latter explains why the former exists. Variations in abiotic and biotic factors are how variety in organisms came to be. Let’s look at what the content focus from the syllabus says:
The course focus is further explored in the core topics:
- Effects of the Environment on Organisms
- Adaptations
- Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
- Evolution – the Evidence
You’ll be asked to use secondary sources a lot, so get ready to open a million tabs. This skill falls under your ‘working scientifically’ skills (so you can show your great research and information consolidation skills).
Haven’t collected study notes for Module 1 yet? Check out our Guide to Year 11 Biology Module 1: Cells as the Basis of Life to make things easier!
Effects of the environment on organisms
Inquiry question: How do environmental pressures promote a change in species diversity and abundance?
An organism’s ecosystem is comprised of abiotic and biotic factors. You’ll learn that these factors can cause changes in diversity and abundance in populations.
Great examples in the Australian environment that the syllabus focuses on are:
- Cane toads which have adapted mechanisms which escape predation and survive despite low water availability. The Australian Museum does a great overview of the rapid spread of cane toads across Australia that you can check out here!
- Prickly pear cactus – more information can be found right here!
Just a tip: make sure you know why these invasive species are a problem to the Australian ecosystem.
Adaptations
Inquiry question: How do adaptations increase the organism’s ability to survive?
Adaptations allow organisms to live fitter than others in a population without it. In this topic, you will use secondary sources to explore adaptations that animals have evolved in response to an environmental selector.
You will need examples of a structural, behavioural and physiological adaptation. When finding examples of adaptations to the Australian environment, think about what the Aussie landscape is like. What kind of animals show adaptations to hot, dry temperatures? What about low availability to food?
Theory of evolution by natural selection
Inquiry question: What is the relationship between evolution and biodiversity?
You’ll be going through quite a few concepts in this module. The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection underpins the concept of adaptations. It is one of the most widely accepted theories, and its pretty important to understand.
You’ll first be learning about what Darwin and Wallace’s Theory of evolution by natural selection is all about. Things like ‘survival of the fittest’ means that the most suitable trait(s) of an organism are pass down to the next generation in face of changes in environments. Great demonstration is moths during the industrial revolution.
Peppered Moths were heavily documented during this period of time.
See it in action here:
Next, you learn about the concept of microevolution which are ways that a population of organisms genes can change (natural selection being one of the ways).
You’ll be also introduced to three concepts:
- Convergent evolution – think lots of different organisms coming to one place, and eventually looking the same
- Divergent evolution – think similar organisms gradually looking different
- Punctuated equilibrium
As you can see, these terms can get confusing. Creating a List of definitions with the terms you’ve created so far can help you remember what words mean. You can Ctrl+F your way into a Band 6!
Evolution – the evidence
Inquiry question: What is the evidence that supports the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection?
Once again, you’ve gotta use secondary sources to analyse various levels of evidence supporting evolution. These include
- biochemical evidence
- comparative anatomy
- comparative embryology
- biogeography
- techniques used to date fossils such as carbon dating
For this part, expect to draw up tables to compare the findings of each method. Note that your headings can be evidence, findings, how findings were found, diagram.
In light of recent medical and health concerns, you’ll get to look at the use of antibiotics, in particular you’ll look at antibiotic resistance. Bacteria essentially evolve in response to antibiotics as the selecting factor.
Check out antibiotic resistance in action here!
Great news, you can use Cane toads as an example here again!
Now that we’ve gone through what the topics are, how can you ace this module and smash it out of the ballpark?
How do I get a Band 6 in Year 11 Biology Module 3: Biological Diversity?
Tip #1: Seeing is believing
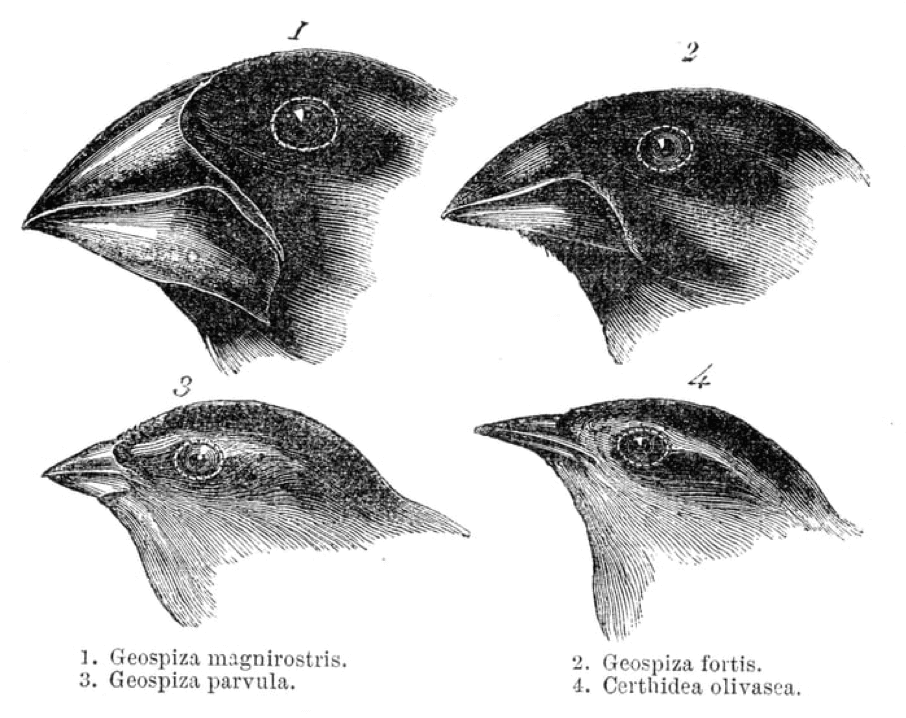
Diagrams, videos and pictures are going to be your best friend in this module. Actually seeing the physical changes that occur as a result of evolution is a great way to understand why the changes have occurred. It’s one thing to know that Darwin’s finches are different, but it’s another to see that sharp beaks were used for insects, and curved beaks were for nuts.
Tip #2: Cane toads and finches
You might have realised that Cane toads and Darwin’s finches are versatile examples you can use for almost all topics. Once you’ve learnt these in depth, you can use them again to demonstrate different aspects of diversity.
Both are great examples of adaptations to new environments. Darwin’s Finches are better examples of divergent evolution.
Tip #3: Questions and past papers
Questions that you can find on forums, in textbooks and past papers are great ways to challenge what you currently know about a topic.
Conclusions
- Learn Darwin’s Finches and Cane toads in depth for a versatile example you can use for any topic
- Asking questions about the topic can drive in what you know and also find any gaps in your knowledge
- Looking at the organisms you are studying is a great way to remember what adaptations they have
On the hunt for other module guides for Biology?
Check out the ones we’ve created below:
- Module 1: Cells as the Basis of Life
- Module 2: Organisation of Living Things
- Module 4: Ecosystem Dynamics
- Module 5: Heredity
- Module 6: Genetic Change
- Module 7: Infectious Disease
- Module 8: Non-infectious Disease and Disorders
Are you looking for some extra help with HSC Biology?
We pride ourselves on our inspirational Year 11 Biology coaches and mentors!
We offer tutoring and mentoring for Years K-12 in a large variety of subjects, with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or at one of our state of the art campuses in Hornsby or the Hills! Get five-star tutoring support in Parramatta!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor get in touch today!
Give us a ring on 1300 267 888, email us at [email protected] or check us out on TikTok!